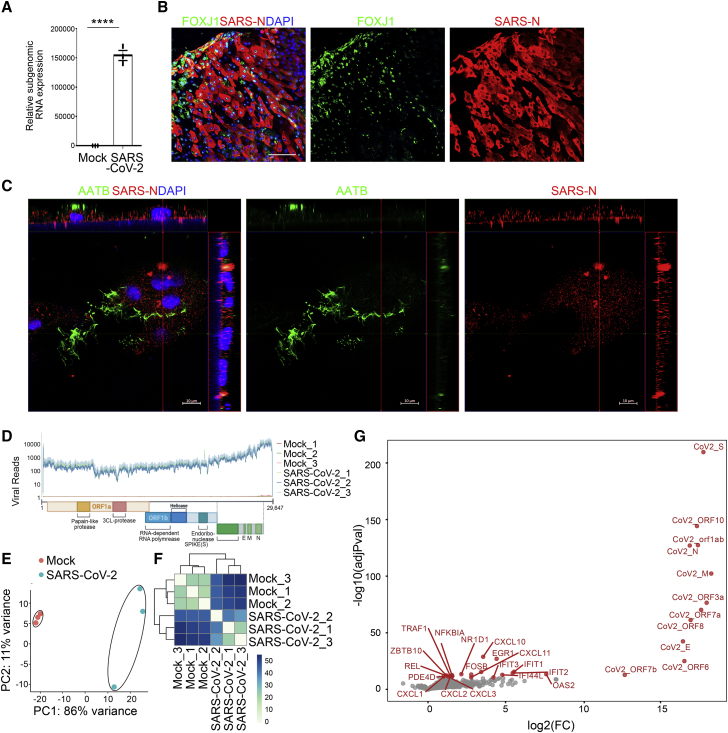
Figure 2.
hPSC-AOs are permissive to SARS-CoV-2 infection
(A) Relative SARS-CoV-2 RNA expression levels in hPSC-AOs at 48 hpi (MOI = 0.2). Total viral RNA from infected hPSC-AOs was analyzed by qRT-PCR for the presence of N transcripts relative to ACTB.
(B) Representative confocal images of hPSC-AOs at 48 hpi (MOI = 0.2) co-stained with antibodies recognizing SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (SARS-N) protein and ciliated cell marker FOXJ1. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(C) Representative 3D confocal images of hPSC-AOs at 48 hpi (MOI = 0.2) co-stained with antibodies recognizing SARS-N and AATB. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(D) Read coverage on viral transcriptome in the mock- and SARS-CoV-2-infected hPSC-AOs (MOI = 0.2). Schematic shows the SARS-CoV-2 genome. Coverage is normalized per million reads.
(E and F) PCA (E) and sample clustering (F) on the mock- and SARS-CoV-2-infected hPSC-AOs.
(G) Volcano plot showing the gene expression changes between mock- and SARS-CoV-2-infected hPSC-AOs.
Data in (A) are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3 biological replicates). The p values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
See also Video S2.