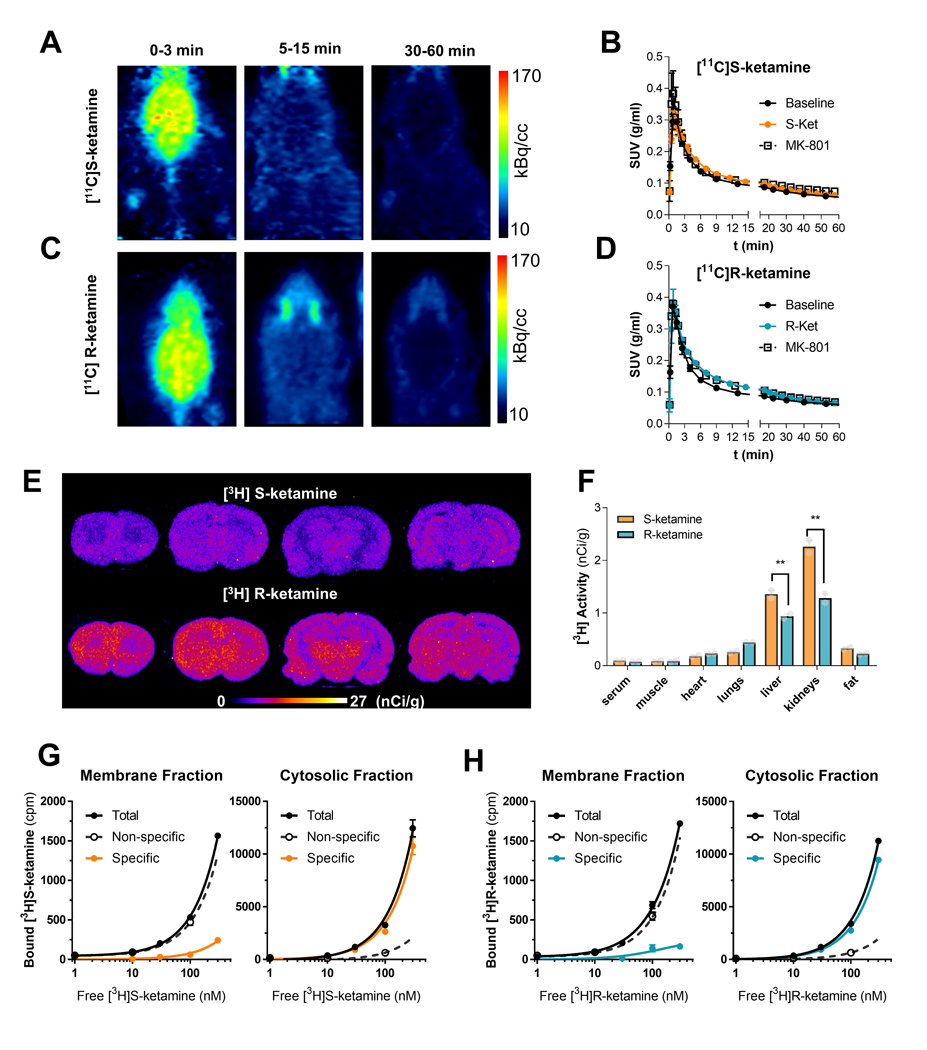
Figure 2. Rapid brain uptake, fast clearance and no high affinity target for ketamine enantiomers.
Representative PET images obtained after bolus IV administration of [11C](S)-ketamine (A) or [11C](R)-ketamine (C) at different time windows. After the initial brain uptake, activity remains exclusively in the harderian glands (nonspecific accumulation). In B and D, whole brain time activity curves measured after a bolus administration of either [11C]-ketamine enantiomer preceded by a pretreatment with the cold enantiomer (10 mg/kg IP) or the NMDAR non-competitive antagonists (+)-MK-801 (0.1mg/kg, IP). Data points are mean ± SD of standardized uptake values (SUV, g/ml) obtained from at least two PET images per condition. In E, representative autoradiograms of coronal brain sections of rats injected (IV, 1μCi/g) with radiolabeled [3H](S)-ketamine and [3H](R)-ketamine and euthanized at 40 min post injection. In F, biodistribution of [3H](S)-ketamine and [3H](R)-ketamine 40 min after IV administration. Saturation binding experiments using membrane and cytosolic fractions of rat brain homogenates indicate the lack of a high affinity specific binding (displaceable and saturable) (G-H).