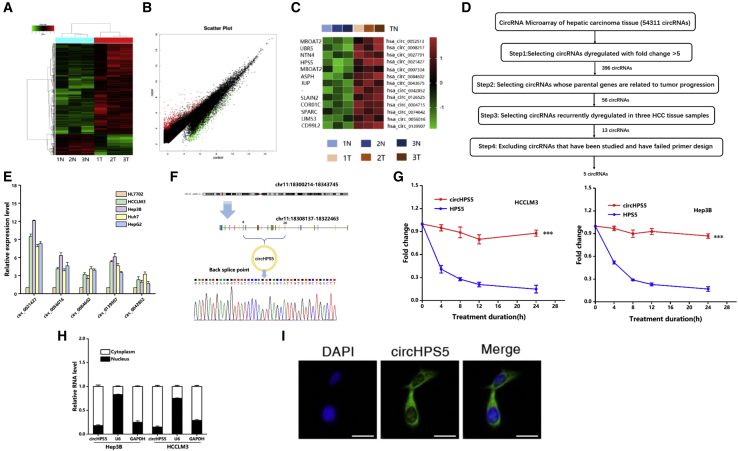
Figure 1.
Characterization and expression of circHPS5 in HCC
(A and B) Cluster map and scatterplot of circRNA microarray data showing differentially expressed circRNAs in the HCC group and normal group. A high expression level is indicated by ‘‘red’’ and a low expression level by ‘‘green’’. (C and D) Flowchart illustrating the screening criteria for potential regulatory circRNAs enriched in HCC. Clustered heatmap showing the dysregulated expression of circRNAs in three HCC samples (the |average normalized fold change| > 5). (E) The expression of five circRNAs was evaluated in HCC cell lines using qRT-PCR. (F) The genomic locus of circHPS5. The expression of circHPS5 was detected by qRT–PCR followed by Sanger sequencing. (G) qRT-PCR analysis to determine the abundance of circHPS5 and HPS5 mRNA in HCC cells treated with actinomycin. (H) Nuclear and cytoplasmic separation experiments showing the distribution of circHPS5. U6 was used as a marker to show efficient nuclear/cytoplasmic RNA separation. (I) RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization for circHPS5. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 10 μm. ∗∗∗p < 0.001.