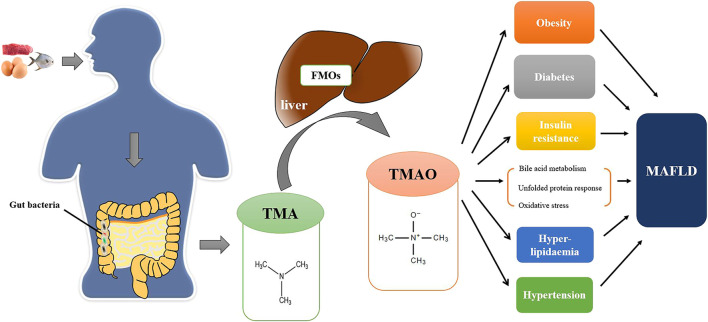
FIGURE 1.
The TMAO pathway in the pathogenesis of MAFLD. Foods (e.g., red meat, eggs, fish, etc.) rich in TMA precursors are digested as choline, L-carnitine, betaine and γ-butyrobetaine in the digestive tract. Excessive TMA precursors that cannot be absorbed are metabolized to TMA by gut bacteria in colon. TMA is then absorbed into the bloodstream through the intestinal mucosa and transformed into TMAO by FMO1 and FMO3 in the liver. TMAO can directly promote the development of MAFLD by affecting bile acid metabolism, unfolded protein reaction, and oxidative stress and indirectly affect the progression of MAFLD by other metabolic disorders (e.g., obesity, diabetes, insulin resistance, etc.).