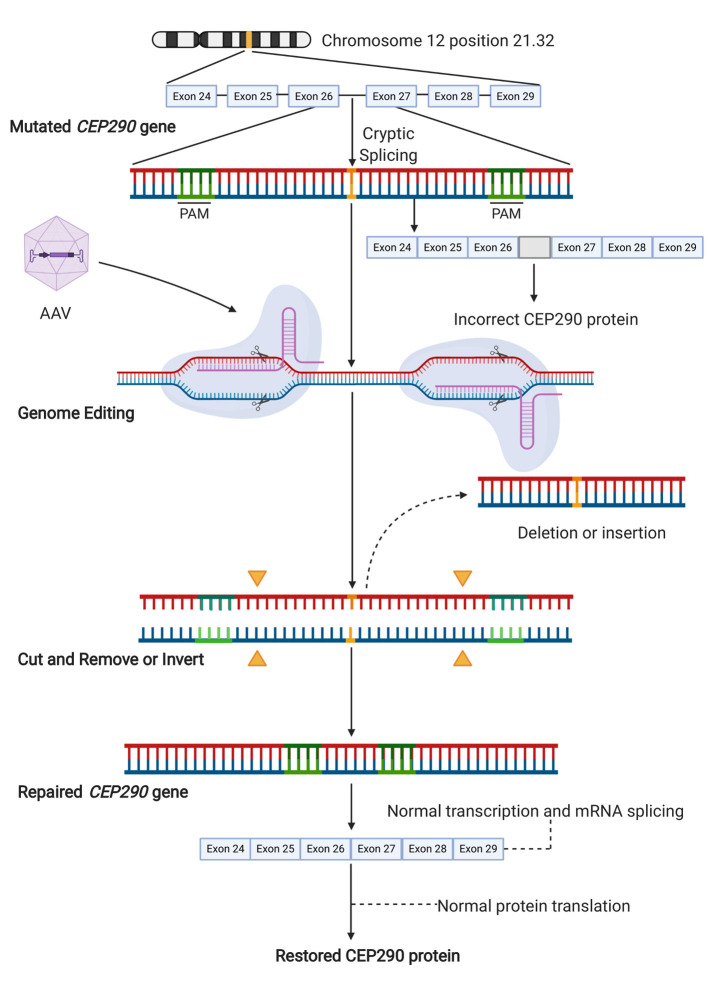
Figure 2.
Gene editing approach targeting the cryptic splice site in CEP290. The pathogenic variant c.2991+1655A>G leads to the generation of a cryptic splice site in the intron between exon 26 and 27. This variant results in the translation of a non-functional mutant protein. Targeted gene editing on each side of the cryptic splice site aims to the removal of this mutation. Successful editing results in either deletion of the DNA segment containing the mutation or its inversion, which similarly results in the loss of the cryptic splice site. This enables the normal translation of functional CEP290 from wild-type full-length mRNA. Illustration created with Biorender software.