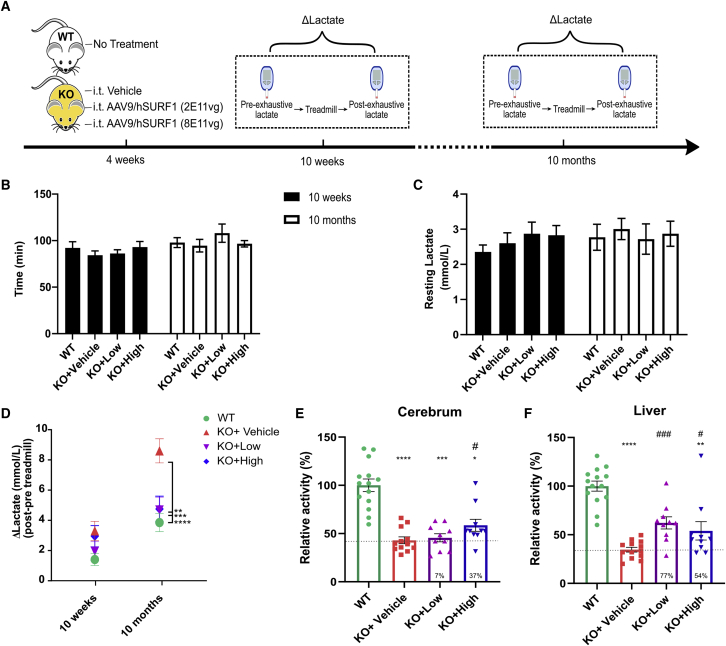
Figure 4.
AAV9/hSURF1 normalized exhaustive exercise-induced lactic acidosis in SURF1 KO mice
(A) Scheme of study design. (B) Running time on treadmill until exhaustion. (C) Resting blood lactate level before treadmill running. (D) Change of lactate after running on treadmill until exhaustion. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 compared with KO+Vehicle mice using a Tukey’s multiple comparison test following two-way ANOVA. (E and F) COX activity of cerebrum (E) (n = 8–10 per group) and liver (F) (n = 9–10 per group) of mice at 18 months of age. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 compared with WT mice using Dunn’s multiple comparison method following a Kruskal-Wallis test, since KO+High mice did not pass the normality test using the Shapiro-Wilk’s test. #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001 compared with KO+Vehicle mice using a one-tailed Student’s t test. A dashed line in (E) and (F) indicates the level of KO+Vehicle, and the percentage of improvement compared with the KO+Vehicle group from each treatment is provided at the bottom of the respective column. Each data point represents measurement from an individual animal, with bars representing the mean ± SEM.