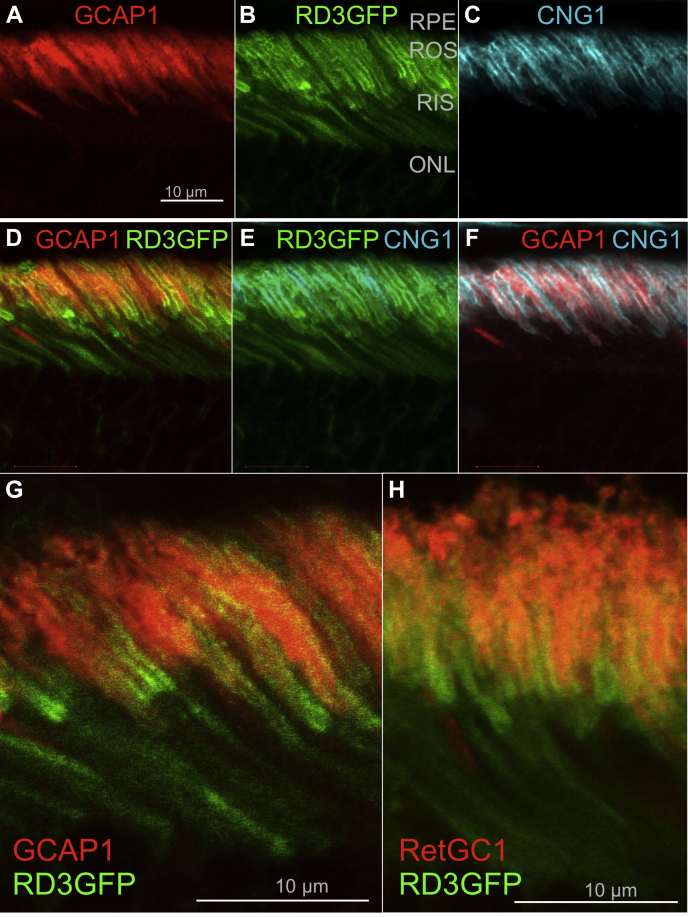
Figure 6.
RD3GFP separates from the RetGC1 and GCAP1 accumulated in ROS.A–F, immunofluorescence in 3.5-week-old RD3GFP+ retinas probed with anti-GCAP1 rabbit polyclonal antibody (red) (A, D, and F) or anti-CNG1 mouse polyclonal antibody (pseudocolored cyan; C, E, and F) in comparison with RD3GFP fluorescence (green; B, D, E, and F); the bar represents 10 μm. G and H, separation of RD3GFP from GCAP1 (G) and RetGC1 (H) immunofluorescence in R838S+RD3GFP+ ROS. The R838S+RD3GFP+ retina sections were probed by rabbit polyclonal anti-GCAP1 (red, G) or RetGC1 (red, H) antibody. Note the similarity between the GCAP1 and RetGC1 localization inside ROS, different in the both cases from the localization of green RD3GFP fluorescence, which is concentrated in the inner segment and near the base of the ROS, partially extending along the plasma membrane but not to the inside of the ROS. CNG, cyclic nucleotide–gated; GCAP, guanylyl cyclase–activating protein; RD3, retinal degeneration-3 protein; RetGC, the retinal membrane guanylyl cyclase; ROS, rod outer segment.