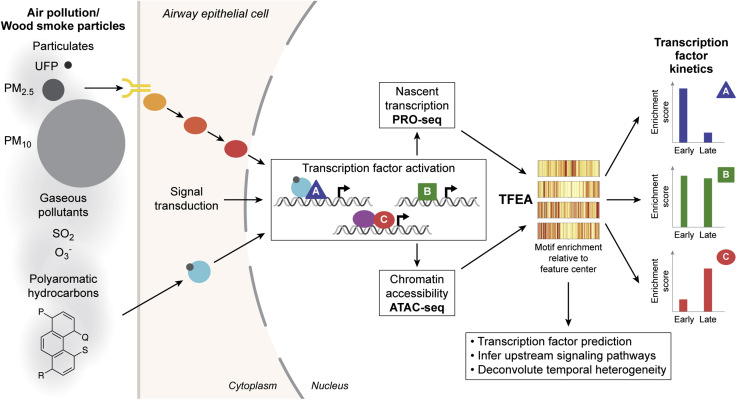
Figure 8.
Genomics-based deconvolution of multiplexed transcriptional responses to complex air pollutants. WSP exposure is predicted to result in complex signal transduction events that lead to activation of multiple transcription factor pathways. To deconstruct these molecular processes, we generated paired genome-wide chromatin accessibility and nascent transcription profiles in response to two WSP exposure time points. Unbiased transcription factor enrichment analysis (TFEA) of these data identified distinct families of transcription factors that mediate changes in gene expression, enhancer activity, and chromatin structure in response to WSP. Transcription factor activity could be further clustered based on timing, and in some cases, responses were rapid and transient. This system can be applied to identify and compare epigenetic and transcription factor responses to different sources of air pollution. WSP, wood smoke particle.