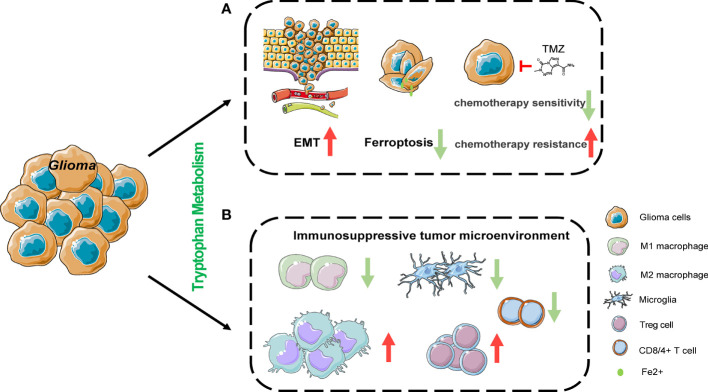
Figure 2.
The effects of tryptophan metabolism in cancer cell and its microenvironment. (A) Tryptophan metabolism mediated by IDO1 and TDO could promote the migration and invasion of glioma cells via Kyn/AHR signaling pathway. IL4I1 catabolizes tryptophan into indole-3-pyruvate (I3P) to inhibit ferroptosis by expressing anti-oxidative gene expression program in Hela cells. IDO1 is induced as an undesired effect of chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer and breast cancer. (B) Tryptophan metabolism suppresses T cell proliferation and function by inducing the differentiation of regulatory T cells (Tregs), the expression of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD1) on CD8+ T cells, cell death of CD8+ T cells and the recruitment of immunosuppressive tumor-associated macrophages. EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition.