Figure 2.
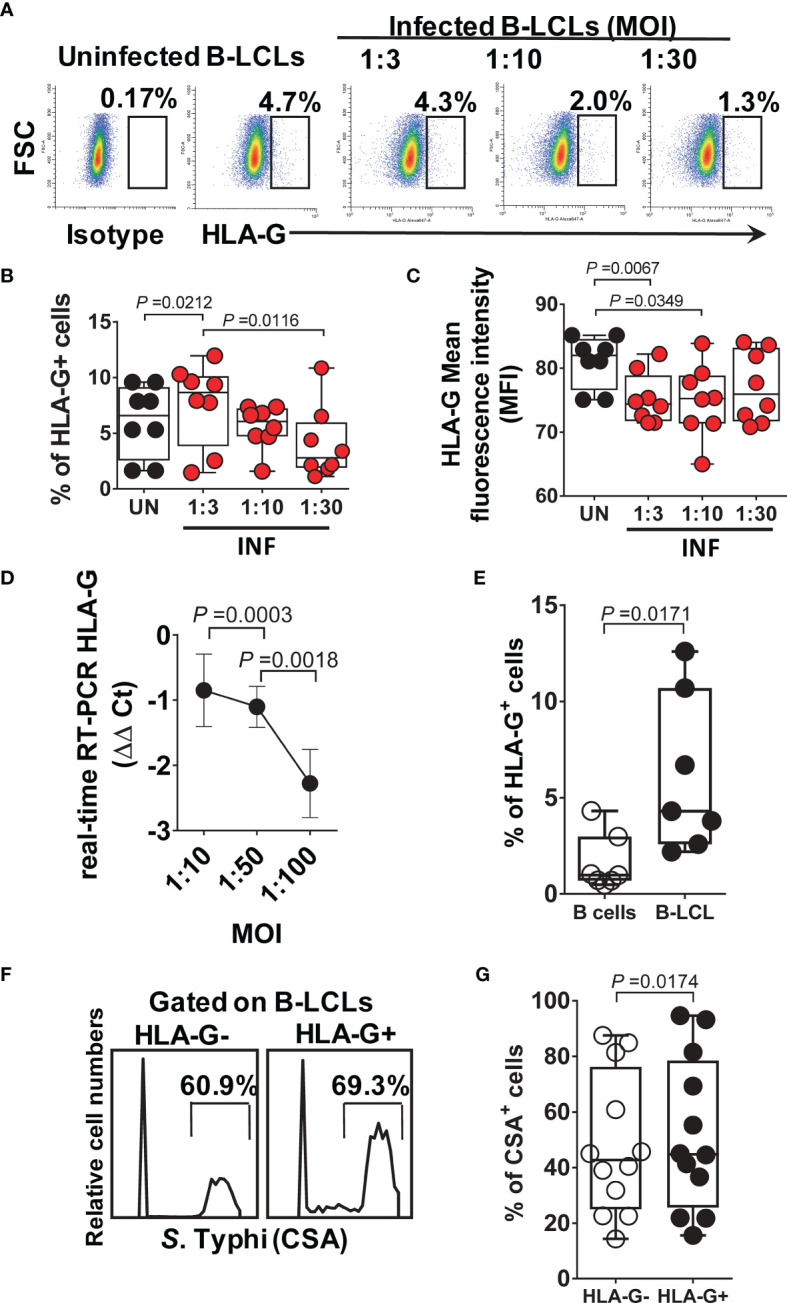
HLA-G expression on B cells. B-LCLs were infected with S. Typhi for 3 hours at different cell:bacteria multiplicity of infection (MOI). Uninfected cells were used as controls. After 16-18 hours of gentamicin treatment, cells were stained with anti-HLA-G mAbs and analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Percentage of B-LCL cells expressing HLA-G on the surface. Cumulative HLA-G (B) percentage and (C) mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). Bar graphs extend from the 25th to 75th percentiles; the line in the middle represents the median of the pooled data. The whiskers delineate the smallest to the largest value. (D) real-time RT-PCR for HLA-G. Data are representative of one out of five independent experiments with one volunteer and six replicates. (E) HLA-G expression on B-LCLs from healthy individuals. Each dot represents one volunteer. (F) S. Typhi infection levels in live HLA-G- and HLA-G+ B-LCLs, Representative experiment. (G) Cumulative % of CSA+ cells. Data are representative of one out of six independent experiments with 4 volunteers and 2 replicates.
