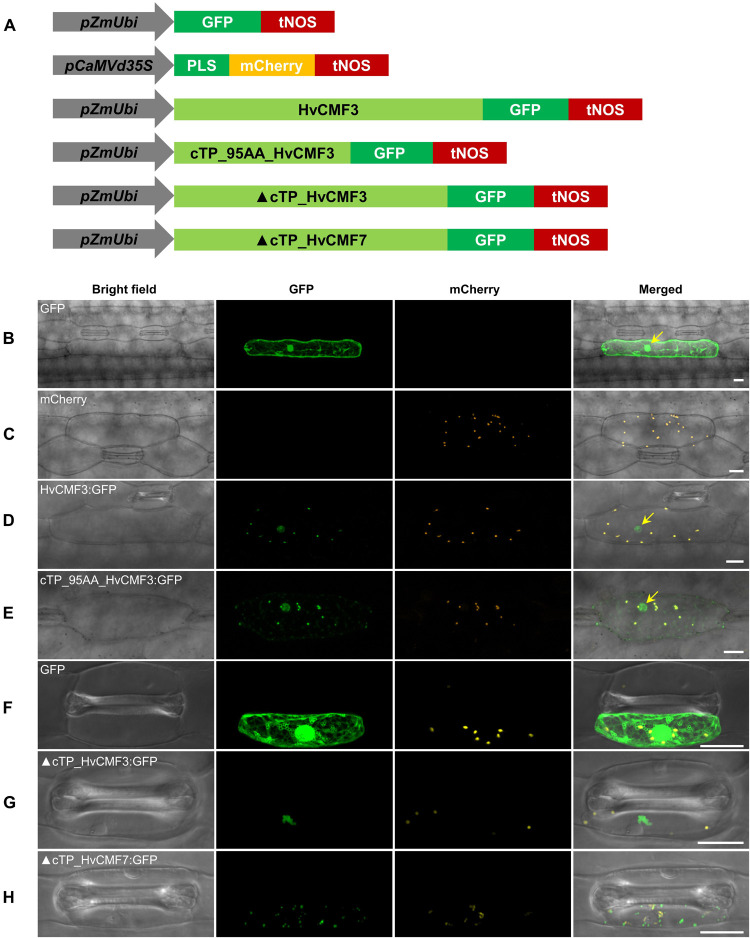
FIGURE 9.
Subcellular localization of HvCMF3. (A) Schematic diagram of the constructs prepared for transient expression. pZmUbi, maize UBIQUITIN1 promoter. pCaMVd35S, Cauliflower Mosaic Virus doubled-enhanced 35S promoter. GFP, green fluorescent protein. mCherry, mCherry fluorescent protein; PLS, plastid localization signal, i.e., the chloroplast transit peptide (N-terminal 79 amino acids) of the small subunit of tobacco RUBISCO. HvCMF3, coding sequence of wild type HvCMF3 gene. cTP_95AA_HvCMF3, N-terminal chloroplast transit peptide of HvCMF3 with a length of 95 amino acids as predicted by online tool PredSL. ▲cTP_HvCMF3, HvCMF3 without N-terminal cTP (T2-T95). ▲cTP_HvCMF7, HvCMF7 without N-terminal cTP (A2-A83). tNOS, Agrobacterium nopaline synthase terminator. The schematic drawing is not in proportion with gene length. The first leaf of 7-day-old barley seedlings was used for particle bombardment. The fluorescence was checked 24 h after bombardment. Scale bar for all images is 20 μm. (B) Localization of GFP control with GFP being driven by the maize UBIQUITIN1 promoter. (C) Localization of the plastid marker. (D) Localization of HvCMF3:GFP. The GFP fluorescence signal is targeted both to plastid and nucleus. (E) Localization of cTP_95AA_HvCMF3:GFP. The yellow arrows in the merged panels indicate the nucleus. (F–H) Localization of GFP control (F), ▲cTP_HvCMF3 (G), and ▲cTP_HvCMF7 (H). Both truncated HvCMF3 and HvCMF7 form aggregates in the cytoplasm.