FIGURE 4.
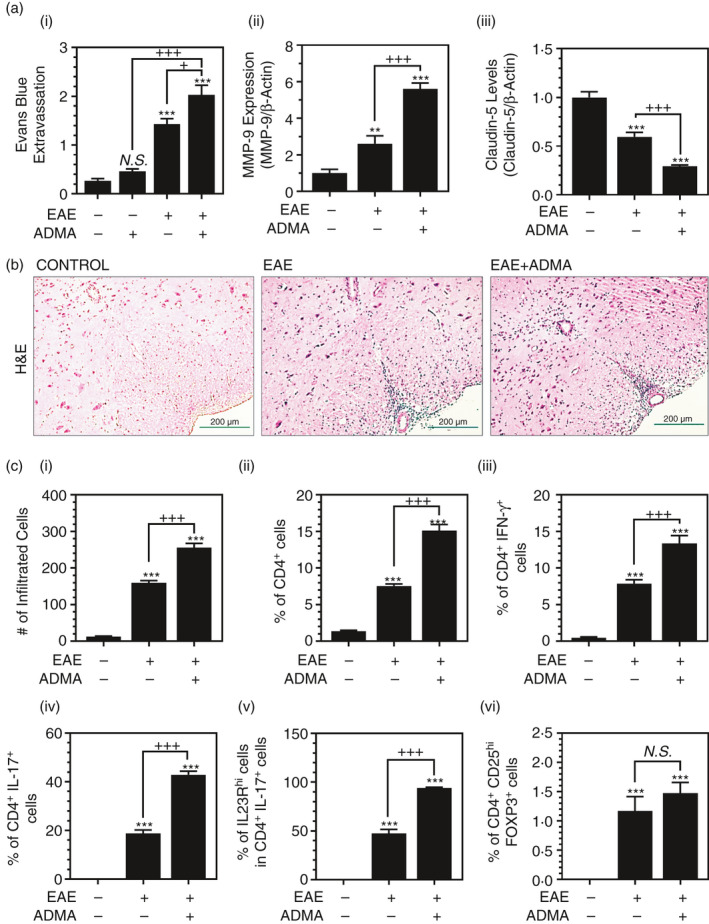
ADMA treatment induces BBB dysfunction and increases CNS infiltration of lymphocytes in EAE mice: Female C57BL/6 mice were treated with complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA), myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) and pertussis toxin (PTX) for induction of EAE with/without daily exogenous ADMA treatment. At the peak of disease (day 19 post‐immunization), the effect of ADMA on EAE‐induced BBB dysfunction, such as Evans blue extravasation into the CNS (brain and spinal cord) (A‐i), and the spinal cord expression levels of MMP‐9 (A‐ii) and claudin‐5 (A‐iii) were analysed. At the peak of disease, infiltration of mononuclear cells into the lumbar area of the spinal cord was visualized as H&E staining (B). In addition, the numbers of infiltrated mononuclear cells (C‐i) and % of CD4+ T cells in CNS infiltrated mononuclear cells (C‐ii), % of IFN‐γ+ TH1 cells (C‐iii) and IL‐17+ TH17 cells (C‐iv) in CD4+ T cells, % of IL‐23Rhi cells in TH17 cells (C‐v), and % of CD25hiFOXP3+ Treg cells in CD4+ T cells (C‐vi) were measured by fluorescent flow cytometry. Please see Figure S1 for the representative flow cytometry dot plots. Data represent mean ± standard error mean (SEM) from n = 6 animals. N.S. (not significant: p ≥ 0·05); *p ≤ 0·05, **p ≤ 0·01, ***p ≤ 0·001 vs. control; +p ≤ 0·05, ++p ≤ 0·01, +++p ≤ 0·001 vs. as indicated
