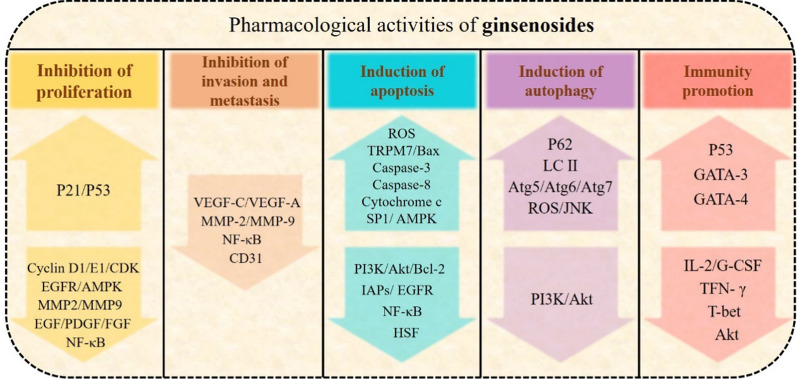
Fig. 3.
Anticancer activities of ginsenosides. The arrow upward in the figure indicates the upregulation of gene expression; the arrow downward indicates the downregulation of gene expression. P21 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, P53 tumor suppressor and transcription factor, CDKs cyclin-dependent kinases, EGFR epidermal growth factor receptor, AMPK 5 AMP-activated protein kinase, MMP matrix metalloproteinase, EGF epithelial growth factor, FDGF platelet derived growth factor, FGF fibroblast growth factor, NF-κB nuclear factor κB, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, CD31 Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1, ROS reactive oxygen species, TRPM7 transient receptor potential melastatin 7, Bax bcl2 associated X protein, SP1 transcription factor Sp1, PI3K phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Akt protein kinase B, Bcl-2 B-cell lymphoma-2, IAPs inhibitor of apoptosis proteins, EGFR epidermal growth factor receptor, HSF the heat shock factor, P62 sequestosome 1, LC3-II the processed form microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3, Atg autophagy-related protein, JNK c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase, GATA T cell specific transcription factor, IL-2 Interleukin-2, G-CSF granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, TNF tumor necrosis factor, T-bet T-box transcription factor