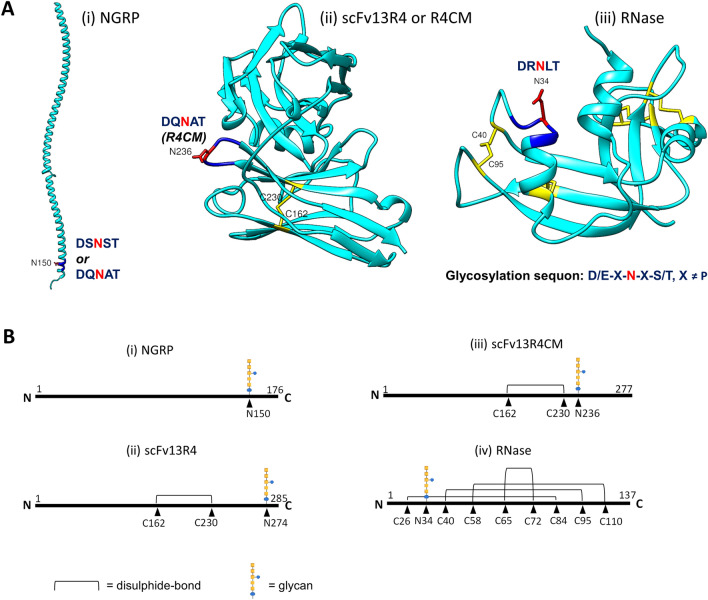
Fig. 2.
Structural variation of model glycoproteins. A Structural models of (i) NGRP, (ii) scFv13R4 and scFv13R4CM were generated by Phyre2 based on protein homology prediction (≥ 99% confidence) [113]. (iii) X-ray crystallographic structure of RNase A (PDB code 3WMR). Ribbon model of the proteins was drawn by UCSF Chimera [114]. Position of the sequon variants (D/E-X-N-X-S/T, X ≠ P) within the protein is indicated. Disulphide-bonds are highlighted in yellow. C-terminal sequon (DQNAT) of scFv13R4 is not displayed in the protein model. B Linear representation of proteins; (i) NGRP, (ii) scFv13R4, (iii) scFv13R4CM, and (iv) RNase A. Position of disulphide-bonds (C–C) and glycosylation sites (N) are indicated with amino acid positions