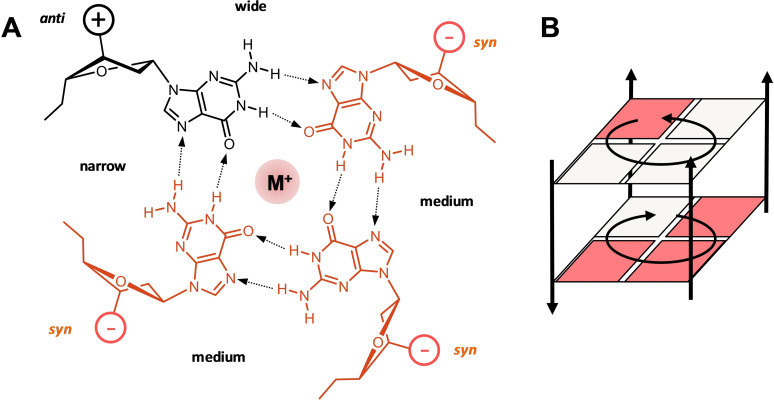
Figure 1.
(A) Planar arrangement of four guanine nucleotides with a central metal ion to form a G‐tetrad. The anti‐ and syn‐Gs are indicated by black and red colors, respectively; the tetrad polarity is determined by the direction of hydrogen bonds with medium, narrow, and wide grooves indicated. (B) Two stacked G‐tetrads of opposite polarity; guanine bases are represented by squares. The syn‐anti pattern in (A) and (B) represent just one example of various possibilities.