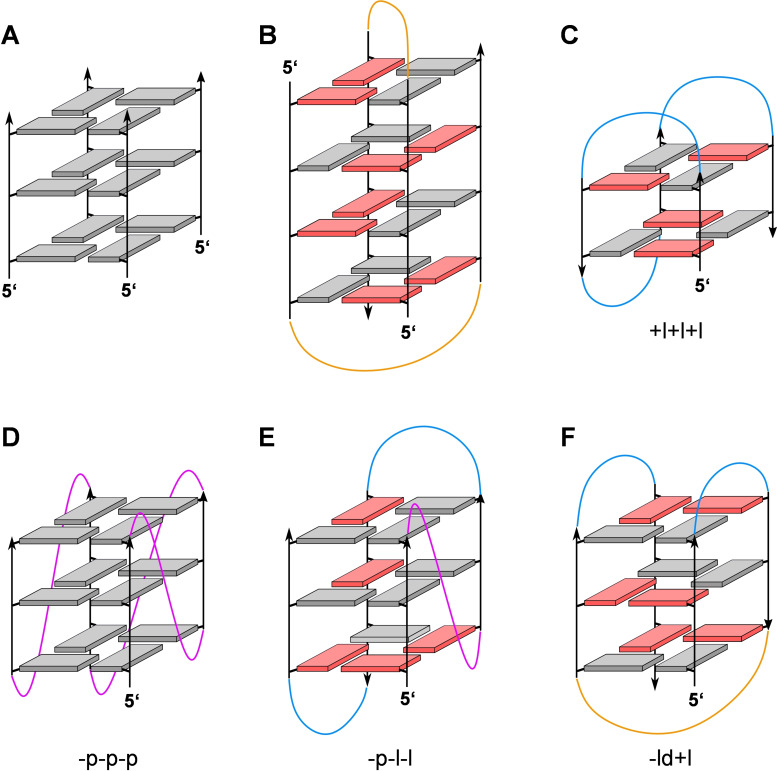
Figure 2.
Representative G‐quadruplex topologies; anti‐ and syn‐guanosines of the G‐core are characterized by grey and red rectangles, respectively; propeller, lateral, and diagonal loops are colored magenta, blue, and orange. (A) Tetramolecular G4 with all strands running parallel and all Gs adopting an anti‐conformation. (B) Four‐layered bimolecular G4 as adopted by d(G4T4G4) in the Oxytricha nova telomere sequence; two diagonal loops connect pairs of antiparallel G‐tracts. (C) Antiparallel ‘chair’‐type topology +l+l+l with two stacked G‐tetrads and three lateral loops running in a clockwise direction as found for the thrombin binding aptamer (TBA) sequence. (D) Monomolecular parallel G4 with three propeller loops progressing in an anti‐clockwise direction (−p−p−p). (E) (3+1)‐Hybrid (hybrid‐1) topology with one propeller and two lateral loops running anti‐clockwise (−p−l−l). (F) Antiparallel ‘basket’‐type topology ‐ld+l with one central diagonal and two lateral loops.