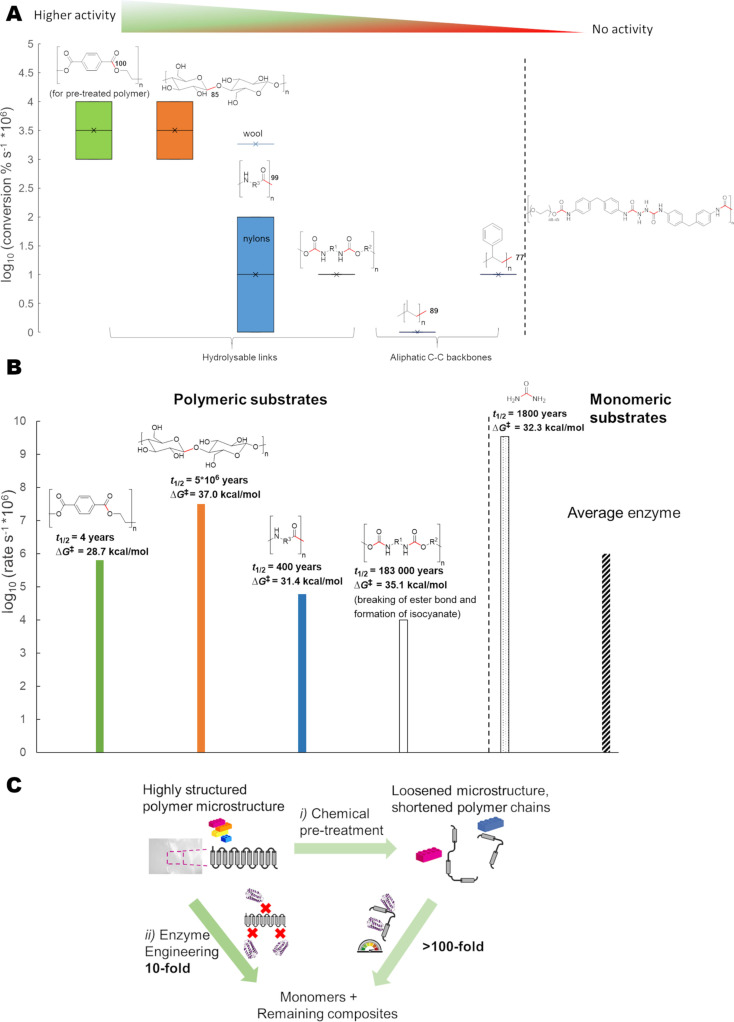
Figure 3.
Biocatalytic activity towards plastics used in the textile industry. (A) Compiled experimental conversion data (given as conversion of polymer per time unit, % s−1) shown as a logarithmic function for clarity. Inherent reactivity of relevant chemical bonds (shown in red) is given as experimentally determined bond dissociation energies [53] [kcal mol−1] of monomeric/oligomeric substrate. For cotton, the bond dissociation energy is represented by a glycosidic ether bond due to lack of experimental data. Experimental data for carbamates was not available as well. Data is shown for (from left to right): pre‐treated PET[ 36a , 36b , 54 ] (green bar), cellulose[ 31 , 55 ] (i. e., cotton, orange bar), nylon[ 41 , 56 ] and wool [23] (blue bar and line, respectively), polyurethane [57] (line, lack of available experimental data prevented calculation of range of conversions). For reference, data for polypropylene[ 47 , 58 ] and polystyrene[ 50 , 51 , 59 ] are given. The structure of spandex is shown (right). For details, see Table S8, Supporting Information and the materials and methods. (B) Enzymatic rate constants [s−1]. Half‐life and free energy of activation (▵G ≠) of uncatalyzed hydrolysis reactions are given at 25 °C, for the relevant scissile bond[ 34 , 60 ] of the corresponding model dimer/oligomer and compiled from experimental data. The uncatalyzed half‐life of 4 years for PET thus reflects the ester bond in monomeric structure and is significantly higher for polymer. Data is shown for (from left to right): pre‐treated PET[ 36a , 36b , 54 ] (green bar), cellulose[ 31 , 55a , 55b , 55c ] (i. e., cotton, orange bar), nylon[ 41 , 56 ] (blue bar), polyurethane [57] (white bar). For reference, data is given for hydrolysis of urea [61] (k cat, dotted bar) and average enzyme proficiency [62] (in terms of k cat, striped bar). For details, see Table S8, Supporting Information and the materials and methods. (C) Potential strategies to increase activities shown in (A) and (B) include pre‐treatment of polymer for enhanced accessibility (in analogy to cellulose degradation) and/or enzyme engineering.