FIGURE 2.
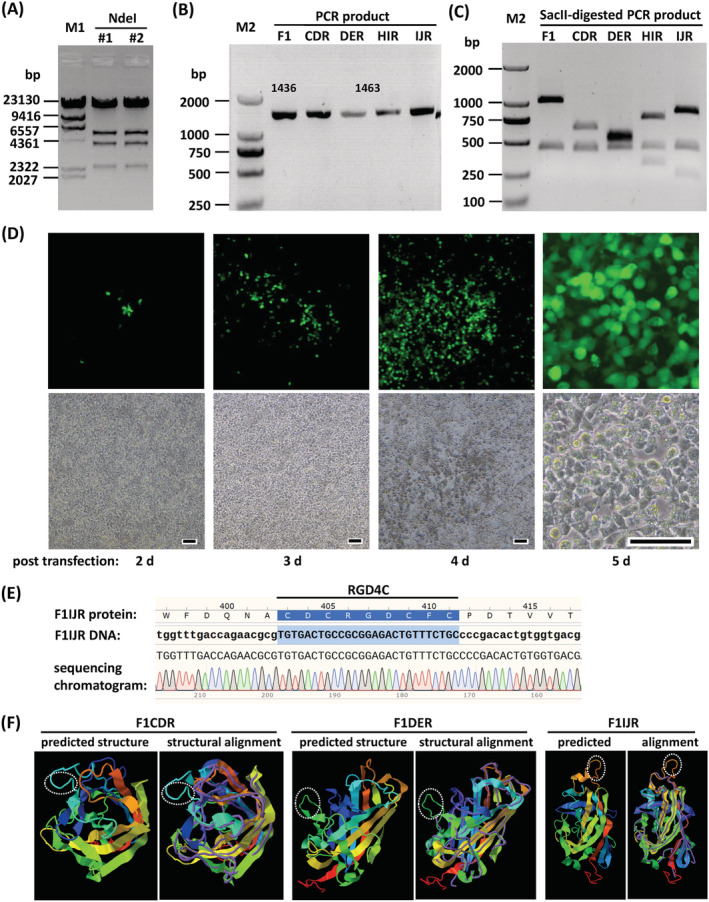
Rescue and identification of fiber‐modified FAdV‐4 vectors. (A) Restriction analysis of adenoviral plasmid pKFAV4F1CDR‐GFP. Plasmids extracted from two bacterial colonies were digested with NdeI and resolved on agarose gel. The expected molecular weights (bp) of the generated bands were 33,944, 5468, 3993, 2352 and 251. (B) PCR amplification of fiber region with adenoviral plasmids as the template and the primers 1805FAV4FMS1/2 (Table 1). The PCR product was 1436 bp for pKFAV4GFP (F1) or 1463 bp for fiber1 modified adenoviral plasmids (CDR, DER, HIR and IJR are short for pKFAV4F1CDR‐GFP and so on). (C) Digestion of above‐mentioned PCR products with restriction enzyme SacII. The expected molecular lengths (bp) of the generated bands were 1007 and 429 for F1; 622, 429 and 412 for CDR; 532, 502 and 429 for DER; 736, 429 and 298 for HIR; and 814, 429 and 220 for IJR. (D) Rescue of FAdV4F1IJR‐GFP (F1IJR) virus in PmeI‐linearized pKFAV4F1IJR‐GFP‐transfected LMH cells. Scale bar = 50 μm. (E) Identification of rescued viruses by sequencing the PCR products of fiber region. A section of the sequencing chromatogram for F1IJR is shown. M1, lambda/HindIII DNA marker; M2, DL2000 DNA marker. (F) Predicted structure of RGD4C‐modified fiber. The amino acid sequences of RGD4C‐modified fiber knob were submitted to the I‐TASSER server for protein structure prediction. The reported model 1 and model‐analog structural alignment for F1CDR, F1DER and F1IJR are shown as representatives. For the structural alignments, query structure is shown in cartoon form, whereas the structural analog (PDB ID 2IUN) is displayed using backbone trace. The RGD4C motifs are marked with dotted ellipses
