Figure 3.
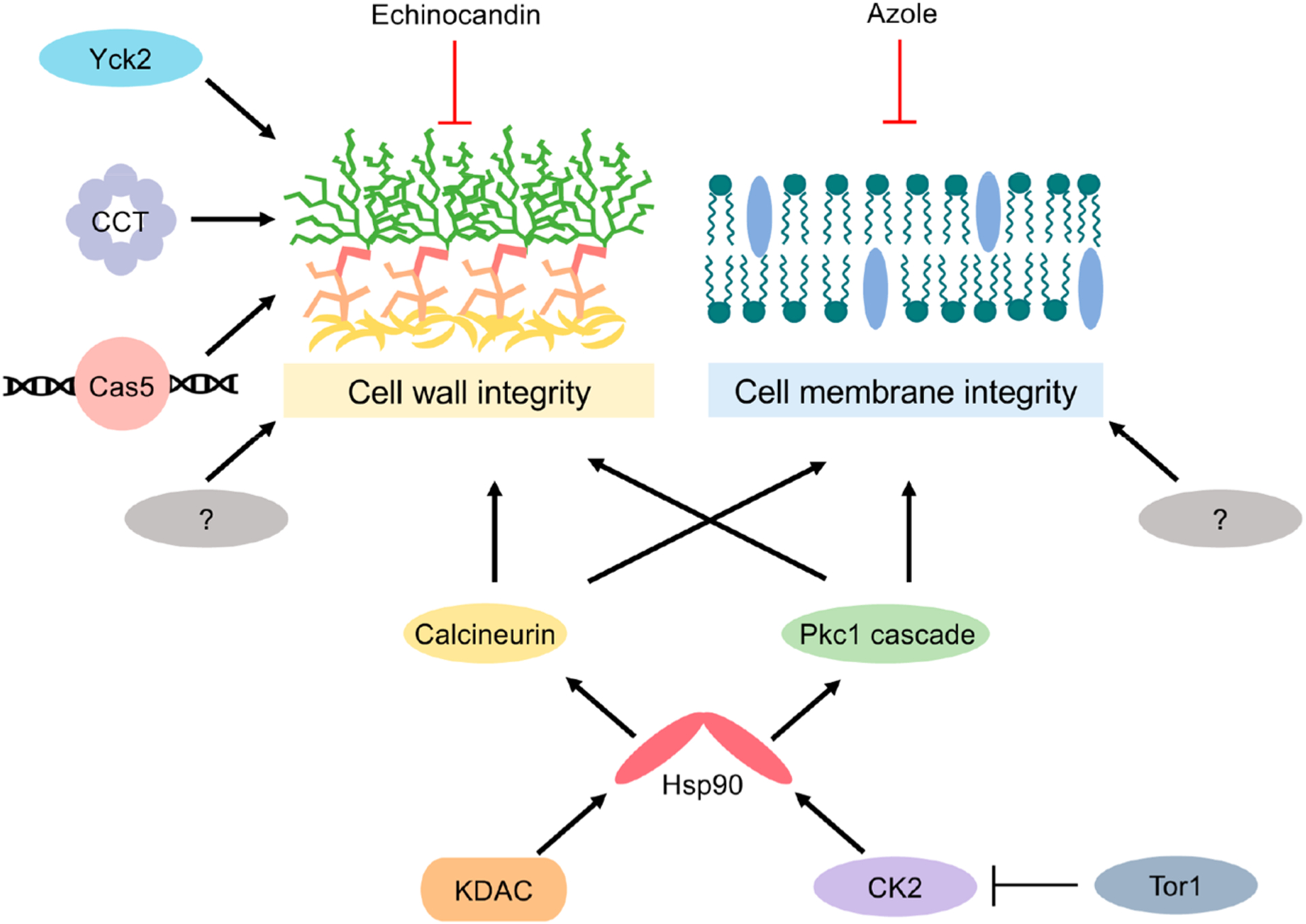
Cellular stress responses important for mediating cell wall and cell membrane integrity. A global cellular regulator governing antifungal tolerance and resistance is the molecular chaperone, Hsp90. In C. albicans, Hsp90 is post-translationally regulated by the protein kinase complex CK2 as well as lysine deacetylases (KDACs). Key client proteins of Hsp90 important for mediating cell wall and cell membrane stress responses include the protein phosphatase calcineurin and several components of the PKC cell wall integrity pathway (Pkc1, Bck1, Mkk2, and Mkc1). Additional cellular factors important for mediating tolerance and resistance to the echinocandins include the transcription factor Cas5, the eukaryotic chaperonin containing TCP-1 (CCT) complex, and the protein kinase Yck2. Notably, many other cellular factors contribute to these cellular stress responses, with many more enigmatic regulators that remain to be identified. Perturbation of any of these signaling pathways in combination with the cell wall or cell membrane stress elicited by the echinocandins and azoles, respectively, culminates in fungal growth inhibition.
