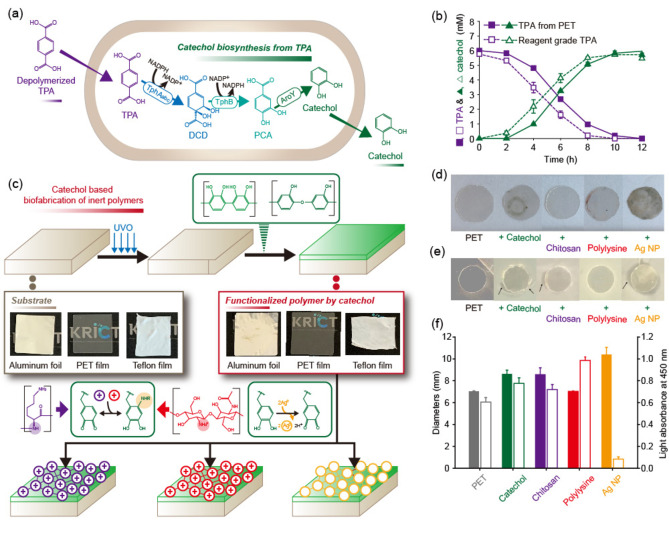
Figure 3.
(a) Bioconversion of TPA to catechol using an engineered E. coli strain. (b) Production of catechol from hydrolyzed TPA and reagent‐grade TPA. (c) General catechol coating process for various substrates (aluminum foil, PET, and Teflon), and the introduction of secondary functional layers on the catechol‐coating: chitosan, polylysine, and silver nanoparticle (AgNP). (d) Picture and (e) E. coli inhibition zone formation of neat PET and catechol only‐, chitosan‐, polylysine‐, and AgNP‐coated PET films. (f) (left) Escherichia coli inhibition zone diameter (negative control, 7.0 mm) and (right) relative L‐929 cell adhesion capacity of neat PET and catechol only‐, chitosan‐, polylysine‐, and AgNP‐coated PET films.