Fig. 2.
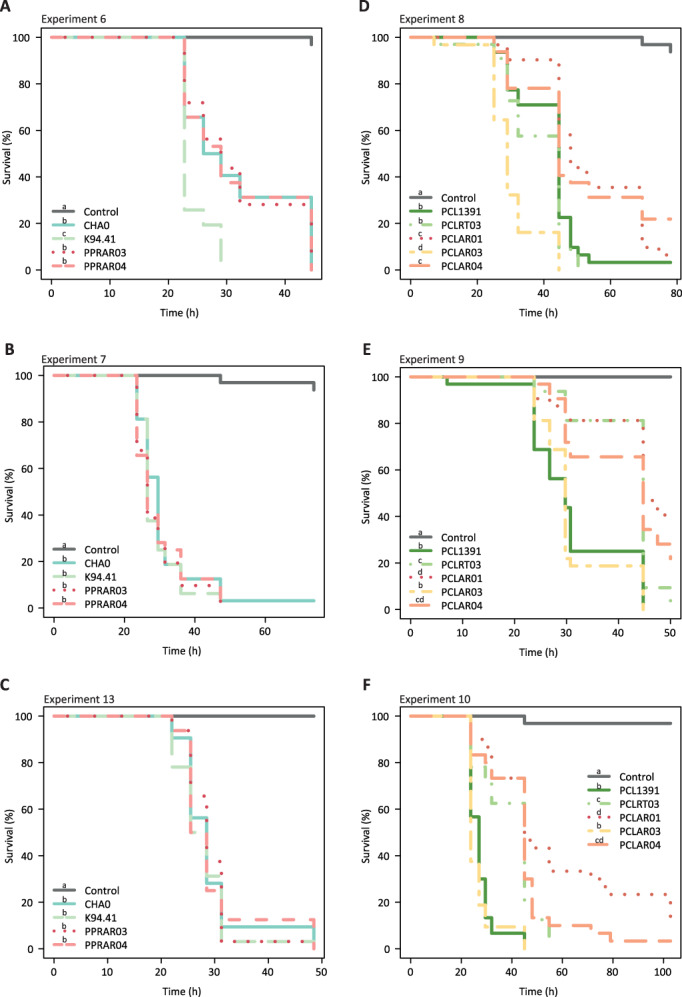
Survival of Plutella xylostella larvae after oral uptake of different Pseudomonas protegens (A, B, C) and Pseudomonas chlororaphis (D, E, F) strains. Second instar larvae were fed with artificial diet pellets spiked with 4 x 106 bacterial cells and mortality was assessed periodically by poking the insects. Strains were isolated from roots (P. protegens CHA0, P. protegens K94.41, P. chlororaphis PCL1391 and P. chlororaphis PCLRT03) or from arthropods (P. protegens PPRAR03, P. protegens PPRAR04, P. chlororaphis PCLAR01, P. chlororaphis PCLAR03 and P. chlororaphis PCLAR04). Statistical differences between the survival of the insects exposed to the different bacteria are depicted as different letters in the legend (Log‐rank test p < 0.05). Thirty‐two larvae were used in each experiment.
