Fig. 4.
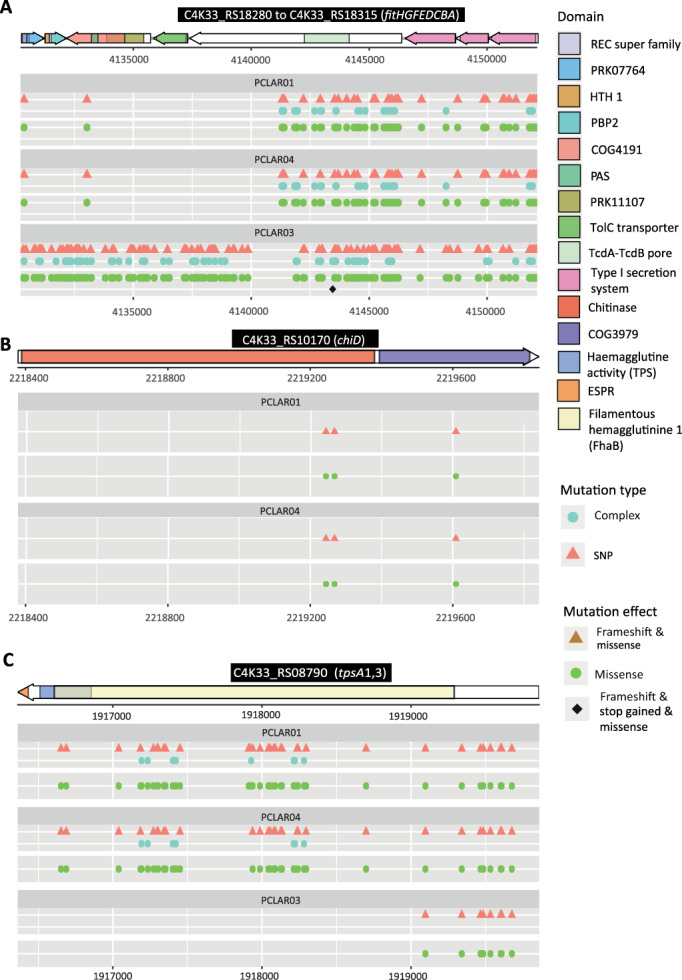
Non‐synonymous variations in the hemagglutinin‐like coding sequences of the gene cluster encoding the insecticidal toxin FitD of P. chlororaphis strains (A), the chitinase ChiD (B) and the two‐partner secretion system TpsA1/3 (A). Genes are depicted by arrows on top of the panels A, B and C, and the protein domain coding sequences are indicated within each gene. Lower panels show the variations harboured by strains PCLAR01 (Coleoptera isolate), PCLAR04 (Coleoptera isolate) and PCLAR03 (Diptera isolate) compared to the genome of the reference strain P. chlororaphis PCL1391. fitHGF are the regulatory genes of the fit cluster. REC: response regulator domain; HTH 1 and PBP2: typical domains of signal transducers; PRK11107 and COG4191: part of a sensor histidine‐kinase; PAS: is a structural domain. The TcdA‐TcdB domain of the FitD toxin is predicted to form a pore in the target cell (Daborn et al., 2002; Waterfield et al., 2003; Ruffner et al., 2015). The fitABCE genes harbour the domains of a type I secretion system predicted to secrete the FitD toxin to the extracellular space. The chitinase domain has the active function of degrading chitin; COG3979: chitodextrinase domain that catalyses the hydrolysis of chitin oligosaccharides. The hemagglutinin activity (TPS) domain is used to interact with the transporter protein for membrane translocation; the filamentous hemagglutinins are repeats used to attach to the host cells and translocate into the host; Filamentous hemagglutinin 1 (FhaB): filamentous‐hemagglutinin domain of Bordetella pertussis; ESPR: signal domain related to type V secretion systems. Mutation type: SNP = single nucleotide polymorphisms; complex = insertions, deletions or larger sequence changes. Mutation effect: modifications that the mutations will cause in the protein, i.e. missense when they cause a change of amino acid and frame‐shift when the translation frame is affected.
