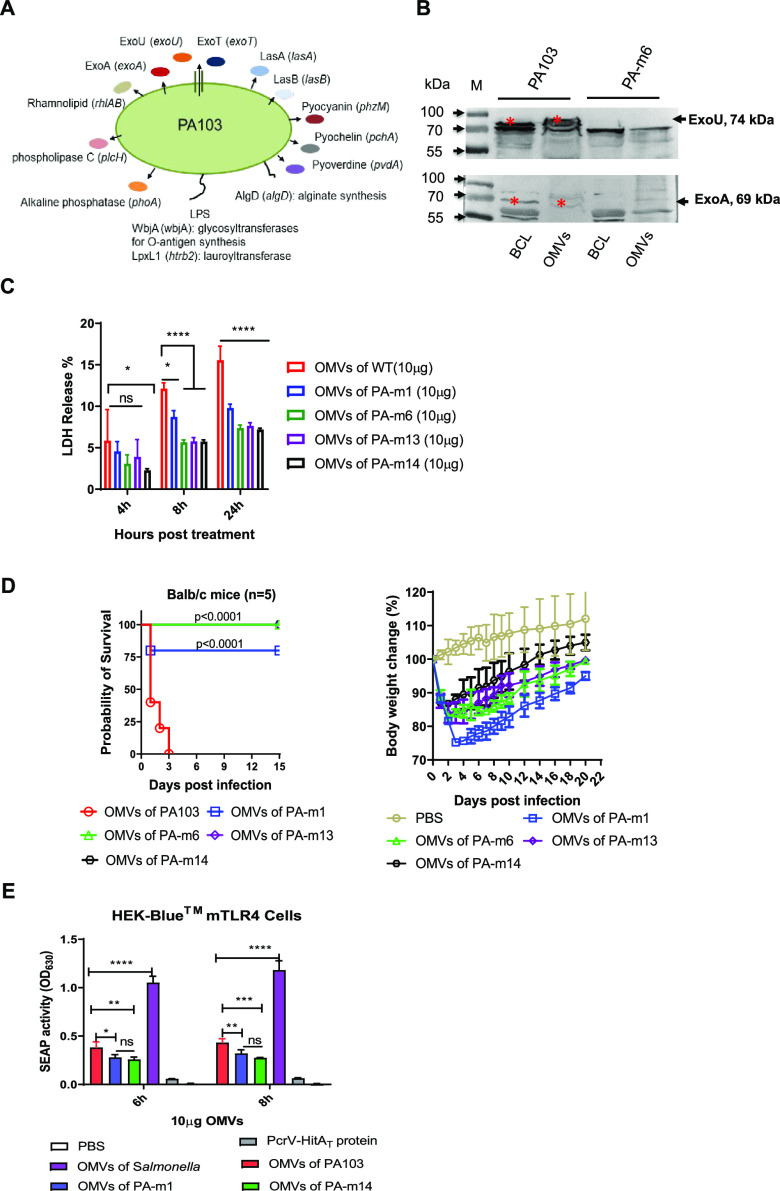
FIG 1.
Analysis of outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) from the genetically manipulated P. aeruginosa strain PA103. (A) Schematic diagram of genes and their encoding proteins. The 14 genes were deleted constitutively to generate the final strain, PA-m14, producing OMVs of low toxicity. (B) Determining the presence of the ExoU and ExoA toxins in a bacterial cell lysate (BCL) and in OMVs from wild-type PA103 or the PA-m6 mutant strain by Western blotting. (C) Quantification of LDH release into culture supernatants of human THP-1 cells treated with 10 μg/ml of OMVs from WT PA103, PA-m1, PA-m6, PA-m13, or PA-m14 for 4, 8, and 24 h (3 replications). PBS was used for a control group. (D) Toxicities of different OMVs from wild-type PA103 or its derived mutants in BALB/c mice. BALB/c mice (n = 5) were injected intramuscularly with 50 μg of OMVs from either wild-type PA103, PA-m1, PA-m6, PA-m11, or PA-m14. Mouse body weight changes after intramuscular injection with OMVs isolated from different strains were measured. Mice were monitored daily for 2 weeks. Statistical significance was analyzed by the log rank (Mantel-Cox) test. (E) TLR4 activation of OMVs in vitro. Secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) activities in HEK-Blue cells with murine TLR4 were compared. HEK-Blue mTLR4 cells (InvivoGen) were cocultured with 10 μg/ml OMVs from WT PA103, PA103 ΔlpxL1, or PA-m14 for 6 or 8 h. OMVs from Salmonella Typhimurium were used as a positive control, and 10 μg/ml of purified PcrV-HitAT protein or PBS was used as a negative control. The statistical significance of differences among the groups was analyzed by two-way multivariant ANOVA with a Tukey post hoc test (ns, no significance; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001).