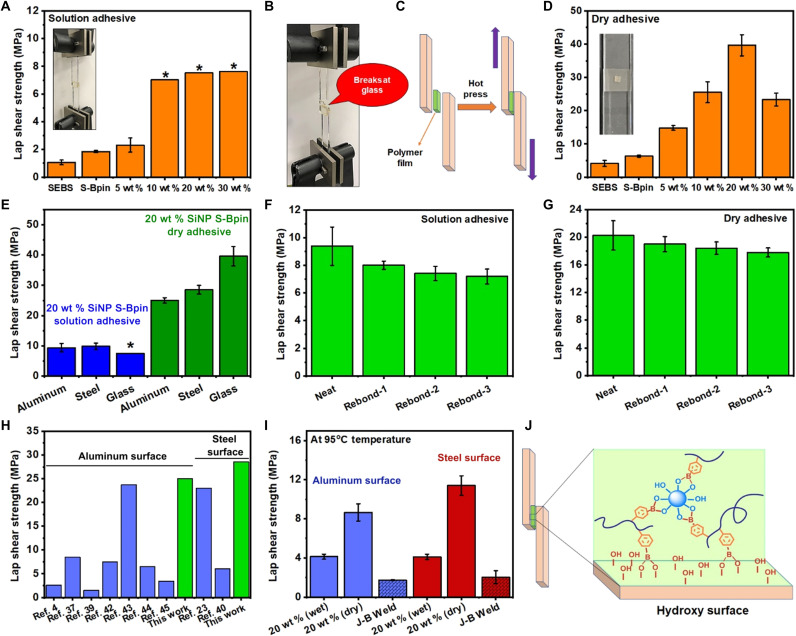
Fig. 5. Lap shear adhesion on glass substrate, adhesive reusability, and comparison to the other adhesives.
(A) Lap shear adhesion on glass surfaces using the composite solution. * indicates that the adhesion could go a much higher value, but we were unable to measure because of glass substrate failure. (B) Lap shear adhesion setup for glass showing the glass fracture rather than breaking the adhesive bonds. (C) Graphical representation of lap shear adhesion test for composite films. (D) Lap shear adhesion on a glass surface using composite films with reduced adhesive cross-section area of (3 mm × 3 mm) 9 mm2 and inset image showing the lap shear adhesion setup. (E) Comparison of adhesive performance of 20 wt % SiNP S-Bpin sample on different substrates. (F) Rebonding ability tests for the 20 wt % SiNP S-Bpin solution on Al surface with adhesive cross-section area of (12 mm × 12 mm) 144 mm2. (G) Rebonding ability tests for the 20 wt % SiNP S-Bpin composite film on Al surface with adhesive cross-section area of (6 mm × 6 mm) 36 mm2. (H) Comparison of lap shear adhesion of dynamic covalent bond–based adhesives reported in literatures (relevant data and references are summarized in table S3). (I) Adhesive performance of 20 wt % SiNP S-Bpin composite solution and dry film on Al and steel surfaces at 95°C. (J) Proposed mechanism of adhesion procedure. Photo credit: Md Anisur Rahman, ORNL. All error bars represent the SD with at least three replicates.