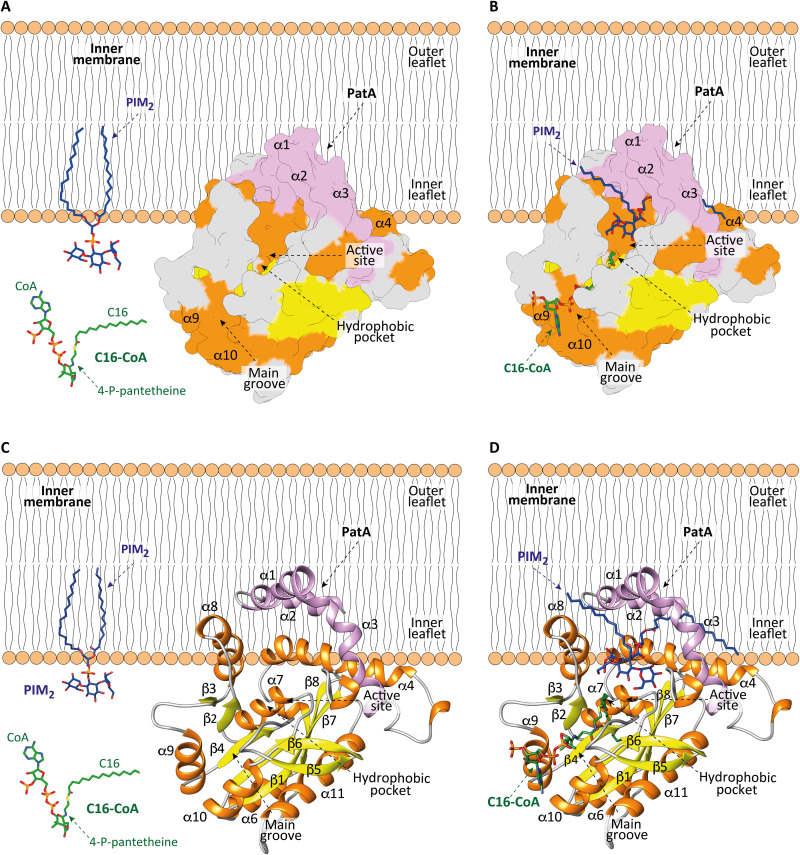
Fig. 7. Model of membrane association mechanism of PatA.
(A to C) The N-terminal helices α1 and α2 and the polarity of PatA determines the right orientation of the enzyme on the membrane. PIM2 is anchored into the inner leaflet of the mycobacterial IM. C16-CoA is localized in the cytosol. (B to D) PatA sequesters the acyl chain of the acyl-CoA donor substrate from the cytosol and incorporates it into a hydrophobic tunnel that extends entirely through the core of the enzyme. In this orientation, the polar head of PIM2 enters into a cavity located in the major groove to react with the acyl-CoA, at the protein-membrane interphase. The Ac1PIM2 product is formed and CoA-SH is released to the cytosol.