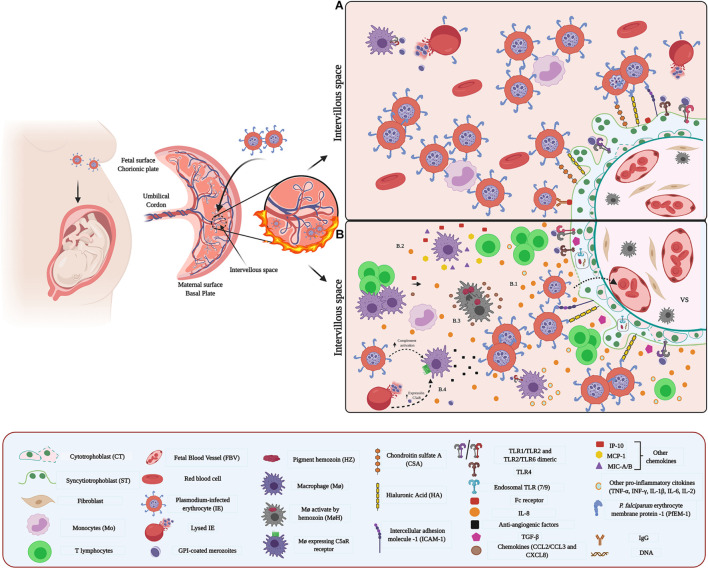
FIGURE 1.
Host–pathogen interaction between Plasmodium and placenta: (A) Adhesion and sequestration of parasite-IEs. IEs express parasite-derived proteins on their surface. For example, the PfEMP1 protein family is highly expressed in placental IEs and acts as a surface antigen and ligand for their adhesion and sequestration. PfEMP1 selectively binds to specific placental receptors such as CSA. Other receptor molecules such as HI and ICAM-1, expressed in ST, participate as key molecules in the adhesion process. (B) Microenvironment and inflammatory response (B.1,B.2) Inflammation in the IVS is attributed to chemokines and cytokines secreted by maternal Mo, T cells, and ST. (B.3) Parasite’s hemozoin induces activation of MΦ, and subsequent release of chemokines. (B.4) Schizonts activate C5 and rupture releasing parasite components containing GPI that induce expression of C5aR and activate MΦ.