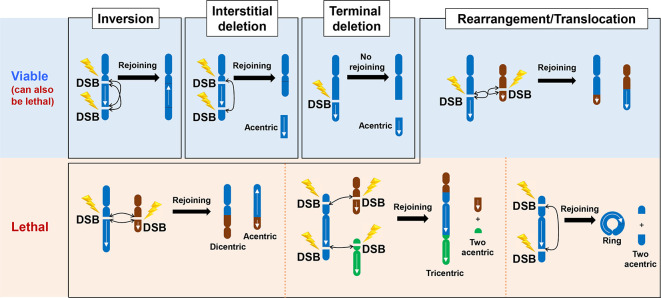
Figure 2.
Mis-repair of the incorrect DNA ends by c-NHEJ in G1 phase to generate chromosome rearrangements. Since we consider mis-repair events arising from c-NHEJ we have focused on chromosome rearrangements in G0/G1 phase cells, where c-NHEJ is the major, and possibly the sole, DSB repair process. Thus, we have shown chromosomes with a single chromatid, which can be visualised using PCC techniques. Failure to repair DSBs in G1 phase can result in terminal or interstitial deletions, translocation events including dicentrics and ring chromosomes. These events are depicted in the figure. Generally, significant loss of chromosome material leads to lethality whilst inversion events or balanced translocations can allow viability. However, some smaller deletions events need not confer lethality, including small interstitial or terminal deletions. The formation of dicentric or ring chromosomes and larger acentric fragments are normally lethal events after cell division. c-NHEJ, canonical non-homologous end-joining; DSB, double strand break.