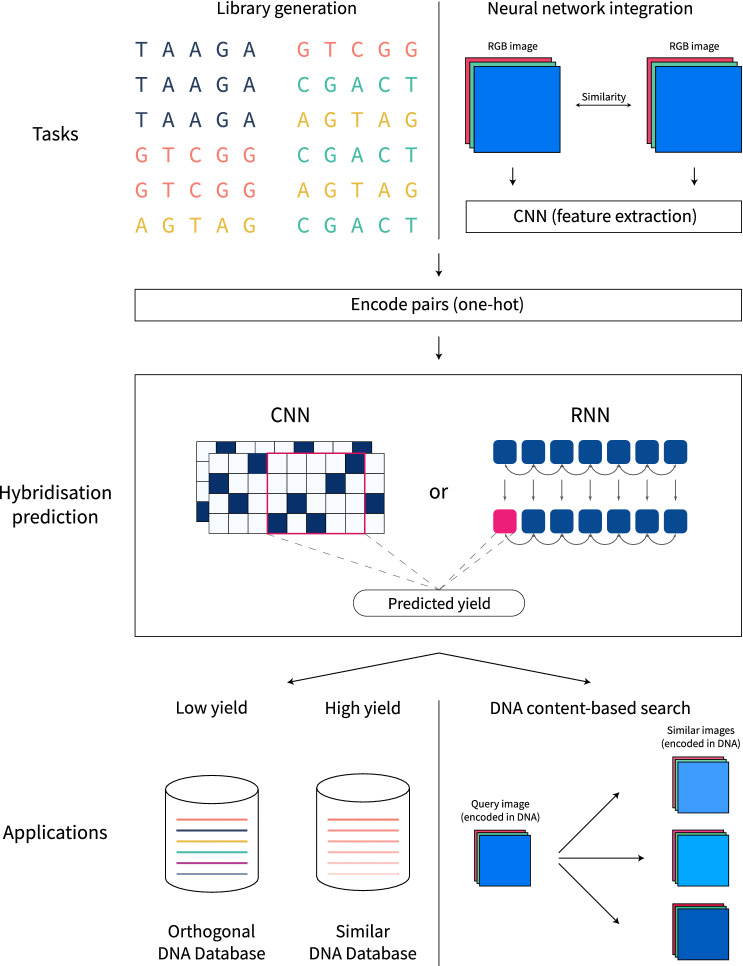
Figure 1.
A high-level overview on how to integrate hybridisation prediction into DNA storage workflows. A trained machine learning model can be used as a standalone tool to assemble orthogonal or similar libraries of DNA sequences (left half of the figure). Alternatively, the neural network can be seamlessly integrated into a larger machine learning model as a subcomponent. The presented example is content-based search in a DNA database, where document features are extracted by a neural network (CNN for images, but text, video or audio inputs are conceivable) in a pairwise manner, another neural component generates appropriate encodings (usually one-hot) and the hybridisation predictor outputs the expected yield of the pair. Such a model is trained to associate similar documents to similar single stranded DNA sequences that form stable duplexes with the query sequence (right half of the figure).