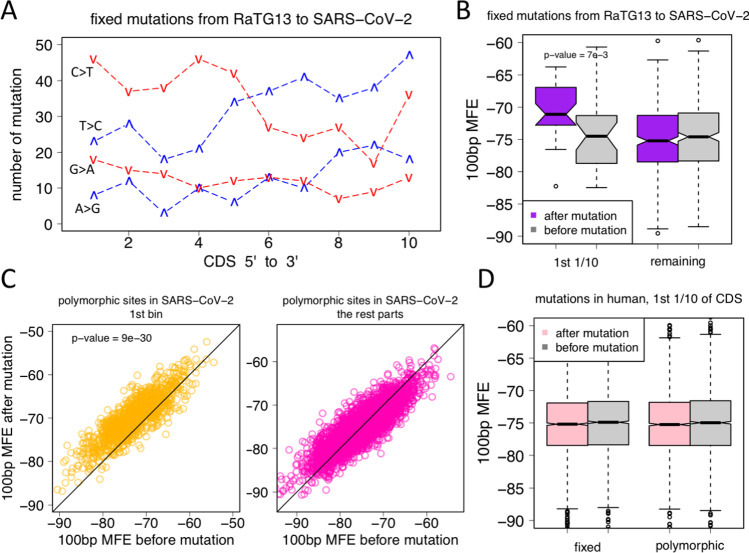
Fig. 4.
Fixed and polymorphic mutations in SARS-CoV-2 or human could change the folding MFE of RNAs. CDS is divided into 10 equal bins as previously described. Comparisons are made between the 1st bin and the other parts. MFE is folded by 100 bp around the focal mutation (from − 50 to + 50 bp). A For the fixed mutations from RaTG13 to SARS-CoV-2, four mutation types are the most abundant (denoted as “from > to”): A > G, G > A, T > C, and C > T. The total number of each type of mutation is counted within each bin. Red lines (G > A and C > T) are the mutations that decrease the GC content. They show high abundance in the 1st bin of CDS. Blue lines (A > G and T > C) are the mutations that increase the GC content. They show depletion in the 1st bin of CDS. B For each of the fixed mutations in SARS-CoV-2, we calculated the MFE before and after mutation. N mutations would have N pairs of observations. p-value was calculated by t-test. C For each of the polymorphic mutations in SARS-CoV-2, we calculated the MFE before and after mutation. N mutations would have N pairs of observations. The sites in the 1st bin of CDS and the remaining parts are compared separately. p-value was calculated by t-test. D For each of the fixed or polymorphic sites in human genome, the MFE before and after mutation were calculated. The sites in the 1st bin of CDS were shown and compared