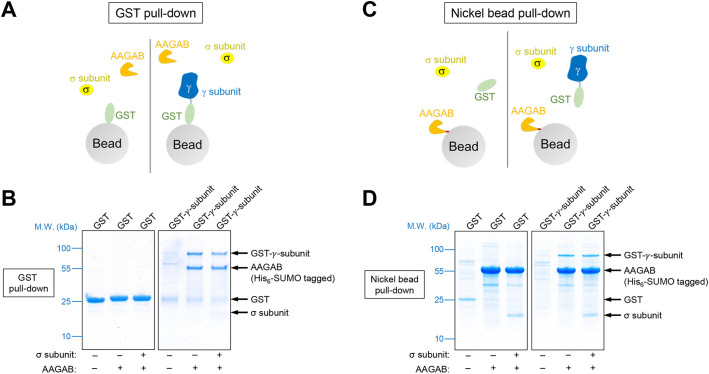
Fig. 6.
AAGAB binds and stabilizes AP1 subunits. (A) Diagram of the GST pull-down assay measuring the interaction of AAGAB with the γ and σ subunits of AP1. His6-SUMO-tagged AAGAB was co-expressed with GST or GST-tagged γ subunit (trunk domain, residues 1–595) in E. coli with or without untagged σ subunit. Proteins were isolated from E. coli lysates using glutathione beads. (B) Coomassie Blue-stained gels showing the binding of GST-tagged γ subunit to His6-SUMO-tagged AAGAB and untagged σ subunit. Note that σ subunit intrinsically stains less because of its small size. Images are representative of three experiments. (C) Diagram of the nickel bead pull-down assay measuring the interaction of GST-tagged γ subunit (trunk domain, residues 1–595) with His6-SUMO-tagged AAGAB and untagged σ subunit. Proteins were co-expressed in E. coli as in A and isolated using nickel beads that recognized the His6 tag of AAGAB. (D) Coomassie Blue-stained gels showing the binding of His6-SUMO-tagged AAGAB to GST-tagged γ subunit and untagged σ subunit. Images are representative of three experiments. M.W., molecular weight.