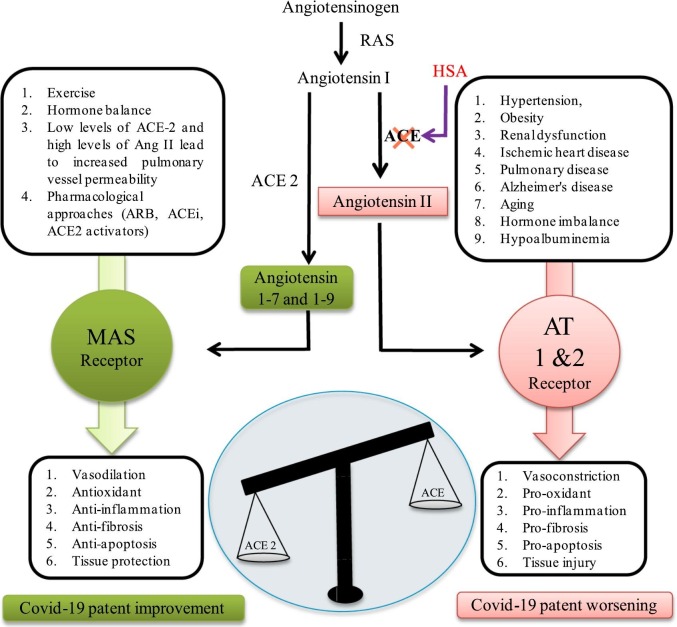
Fig. 4.
The increased ACE/ACE2 proportions have high risk of worse outcomes in COVID-19 infection. In physiological conditions, the ACE metabolizes angiotensin I (Ang I) to angiotensin II (Ang II), consequently leading to increased inflammation ACE 2 inactivates Ang I by generating angiotensin 1–7 and 1–9 (Ang 1–7, 1–9), which at that point binds with the G-protein-coupled receptor Mas. This interaction process is known to be vasoprotective, since it antagonizes the actions of Ang I. However, SARS-CoV-2 downregulates the expression of ACE2, thus leading to RAAS over activation and to increased lung damage and edema.