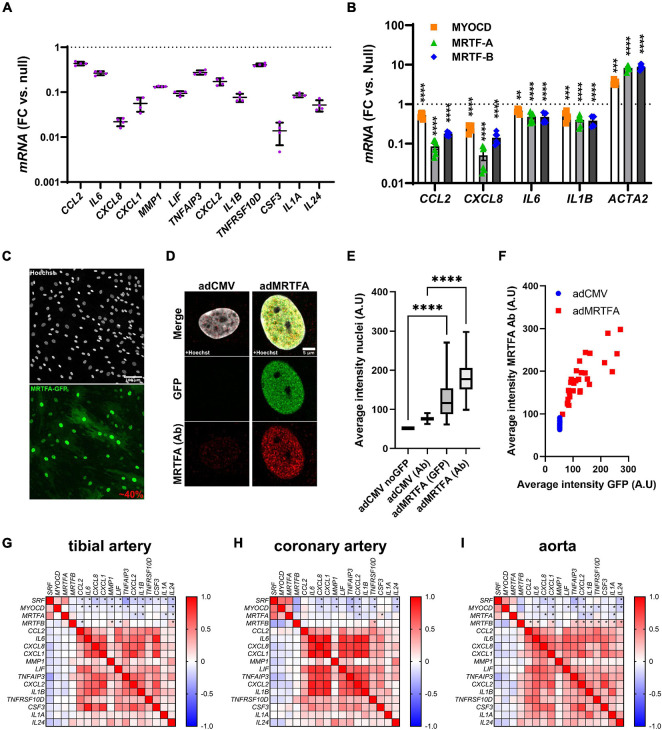
FIGURE 1.
Anti-inflammatory effect of all MRTFs in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells (SMCs). (A) Shows mRNA levels for 13 inflammatory mediators in cultured human coronary artery smooth muscle cells (hCASMCs) after myocardin overexpression using an adenovirus (Ad-CMV-MYOCD). FC: fold change; null: Ad-CMV-null virus. Data is from an RNA-sequencing experiments conducted in a parallel study, and the control level is indicated by the dotted line. All changes were significant at an adjusted P < 0.0001. Suppression of inflammatory markers by myocardin (MYOCD) confirms previous studies and stimulated us to consider if this property is shared by all MRTFs. Side-by-side adenoviral transductions suggested that MTRF-A and MRTF-B have the same effect in the same cell type (hCASMCs, (B)). Confocal imaging showed that 40% of the cells were positive for overexpressed MRTF-A as shown using an eGFP tagged construct (C) and a general nuclear stain (Hoechst). In (D), overexpressed and endogenous MRTF-A were labeled separately using the eGFP tag and an antibody, respectively. Quantification showed that nuclear labeling increased after viral transduction (E), as expected, and the nuclear intensity of labeling in the GFP channel increased linearly with MRTF-A antibody staining (F). We also examined correlations at the mRNA level in human arteries (G–I). RNA-seq data was downloaded from the GTExPortal.org and correlation matrices were generated in GraphPad Prism using the Pearson method. Negative correlations (negative R-values, blue fills) were seen for SRF and MYOCD vs. inflammatory mediators in all arteries. Significant correlations are indicated by (*) for the first four rows in each matrix. MRTFA performed less well than MYOCD and SRF with only a handful significant and negative correlations in each artery. MRTFB performed poorly, and in this case many correlations were positive. These findings suggested a more pronounced anti-inflammatory impact of MYOCD, and MRTFA compared to MRTFB in the intact human vascular wall, despite similar effects upon overexpression in vitro. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.