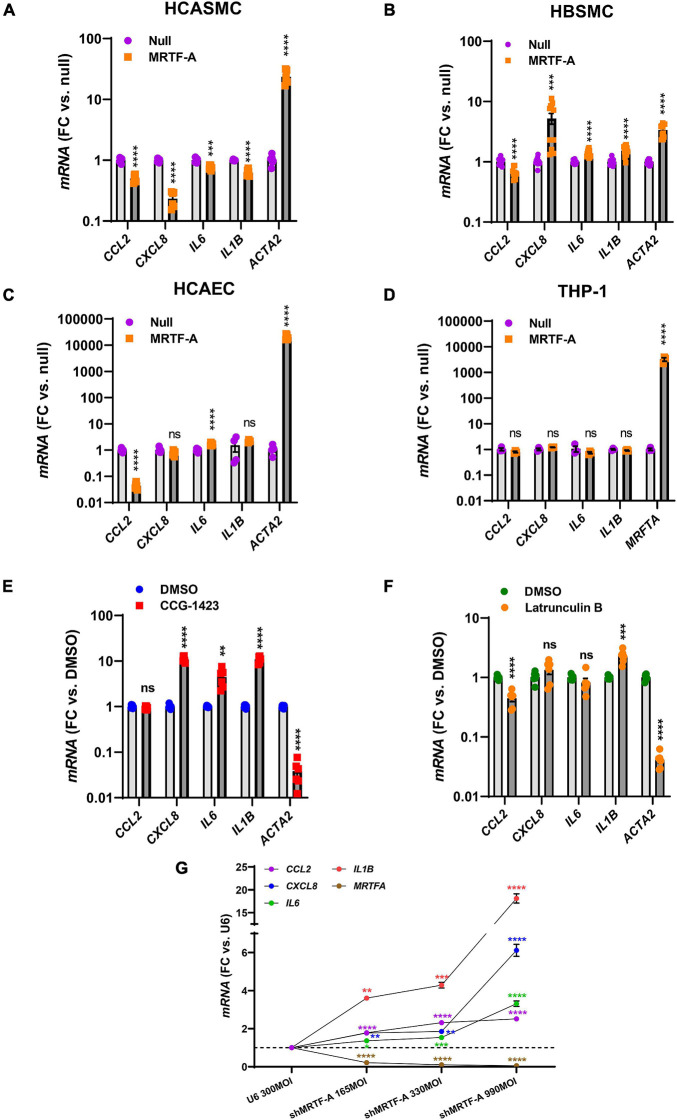
FIGURE 3.
The anti-inflammatory impact of MRTF-A is cell type-dependent. To compare the impact of MRTF-A on inflammation in different cell types, MRTF-A was overexpressed using an adenoviral vector, and using a null vector as control. (A–D) Show the effect of MRTF-A on CCL2, CXCL8, IL6, and IL1B in human coronary artery SMCs (hCASMC, (A)), human bladder SMCs (hBSMC, (B)), human coronary artery endothelial cells (hCAEC, (C)), and monocytes (THP-1 cells, (D)). ACTA2 was used as positive control in all panels except for THP-1 cells where we instead assayed MRTFA itself. (E) Shows the effect of the MRTF inhibitor CCG-1423 (10 μM) in hCASMC transduced with MRTF-A. (F) Shows the effect of Latrunculin B (100 nM), which depolymerizes actin, on the inflammatory transcripts in hCASMC. (G) Shows inflammatory mediators determined by RT-qPCR after silencing MRTF-A using different titers of a short hairpin virus (shMRTF-A). In this experiment U6 represents the control virus. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.