Figure 3.
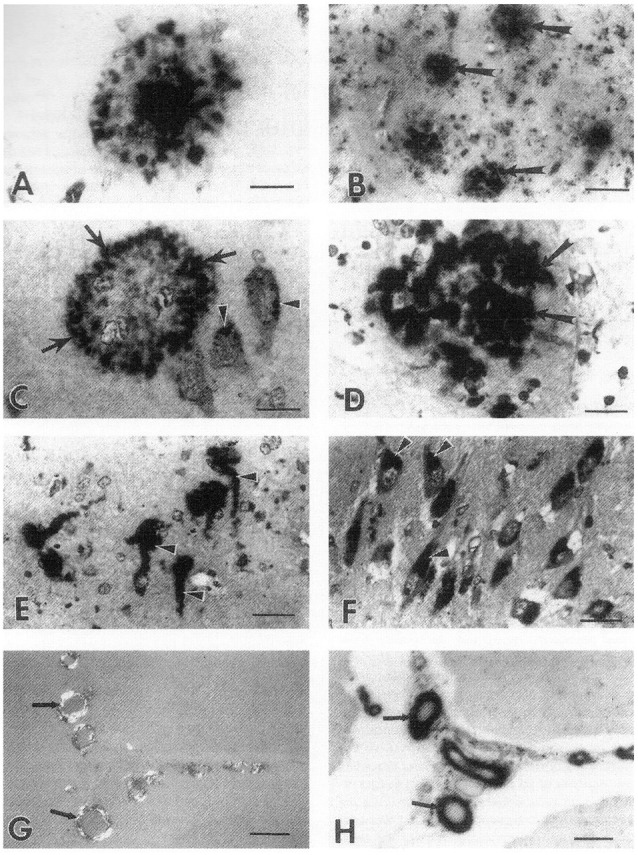
Immunolocalization of heparan sulfate GAGs in neurons and in the characteristic lesions of AD. (A) immunostaining of an amyloid plaque in the hippocampus of a 90-year old woman with AD (obtained 5.5 h after death using the monoclonal antibody (HK-249) recognizing HS GAG chains. Bar, 21 μm. (B) Immunostaining of primitive plaques (arrows) in the amygdala of a 64-year old man with AD (4 h after death). Bar, 80 μm. (C) Heparan sulfate GAG immunostaining (HK-249) in the periphery (arrows) of a primitive plaque in the hippocampus of a 90-year old woman with AD (5 h after death). Note HS immunostaining also in the cell bodies of adjacent neurons (arrowheads). Bar, 20 μm. (D) Strong immunostaining of a primitive plaque using HK-249 antibody in the hippocampus of a 67-year old man with AD (5.5 h after death). Note immunostaining of neurites in plaque (arrows). Bar, 20 μm. (E) Heparan sulfate GAG immunostaining (HK-249) of neurofibrillary tangles (arrowheads) in the amygdala of a 64-year old man with AD (4 h after death). Bar, 40 μm. (F) Strong immunostaining in the cell bodies of neurons (arrowheads) using the HK-249 HS GAG chain antibody in the hippocampus of a 90-year old woman with AD (5.5 h after death). These neurons do not contain tangles because on adjacent serial sections they were negative for Congo red staining, Bar, 40 μm. (G) Positive Congo red staining of meningeal blood vessels (arrows) in the cerebellum of a 74-year old man with AD indicating the presence of cerebrovascular amyloid in these vessels, Bar, 108 μm. (H) Serial section of tissue shown in (G) demonstrates HK-249 HS GAG immunostaining in meningeal blood vessels containing amyloid deposits (arrows). Bar, 108 μm (Snow et al., 1990b).
