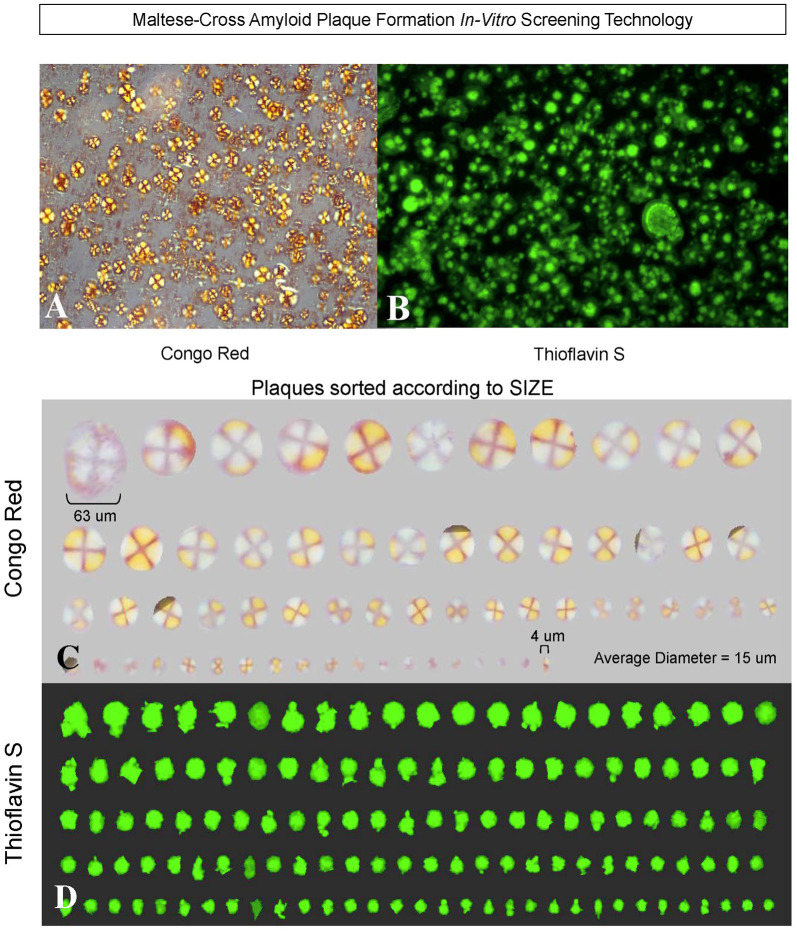
Figure 8.
Heparan sulfate GAGs induce Aβ 1–40 (but not Aβ 1–42) to form spherical congophilic and thioflavin S maltese-cross amyloid plaques identical to those seen in AD brain. Heparan sulfate GAGs + Aβ 1–40 (but not Aβ 1–42) at 1:8 molar ratio (i.e., 50 μg Aβ 1–40 in 100 μl of distilled water with 400 μg of heparan sulfate) spontaneously form (within minutes) spherical congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques (A) and Thioflavin S plaques (B) identical to those observed in AD brain. Spherical maltese-cross amyloid cores were not observed with Aβ 1–40 or Aβ 1–42 alone. (C) Congo red plaques formed by Aβ 1–40 + heparan sulfate GAGs sorted according to size, ranging from 4 μm up to 63 μm, with an average diameter of 15 μm. Note the red-green birefringence of the amyloid cores as viewed under polarized light. Rotation of the polarizer changes the red color to green, and the green color to red (i.e., red/green birefringence). This also occurs identically in the human AD brain following staining with Congo red and viewing brain sections under polarized light. (D) Thioflavin S fluorescence demonstrating the various sizes of amyloid cores formed after incubation of Aβ 1–40 + heparan sulfate GAGs (Castillo and Snow, 2006).