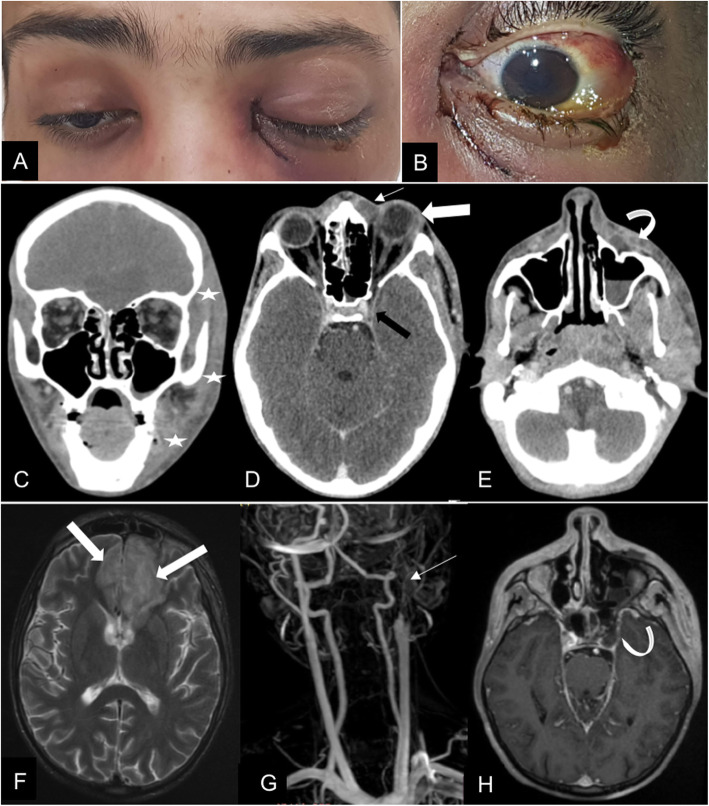
Fig. 1.
A 20-year old COVID-19-affected patient presented with rhino-orbitocerebral mucormycosis. (A) Complete blepharoptosis and inflammatory signs are seen on the left side. There is a mild proptosis on the right side. (B) Note the conjunctival injection, the chemosis and the corneal oedema. (C) Coronal and (D, E) Axial contrast-enhanced brain CT scan show thickening with infiltration of left hemiface fat planes (white stars); left pre-septal collection (arrow) with exophthalmos and lengthening of the antero-posterior axis of the eyeball (large arrow). This collection reaches the cellulo-fatty tissues next to the left maxillary sinus (curved arrow), the latter is the site of a partial liquid filling. The left cavernous sinus shows signs of thrombosis (black arrow). (F) axial T2 weighted image MRI showing T2 hypersignals (large arrow) in areas of the frontal lobes confirming endocranial extension. (G) MR angiography shows left carotid artery thrombosis (arrow). (H) 3D T1 weighted sequence with contrast shows left cavernous sinus thrombosis (curved arrow)