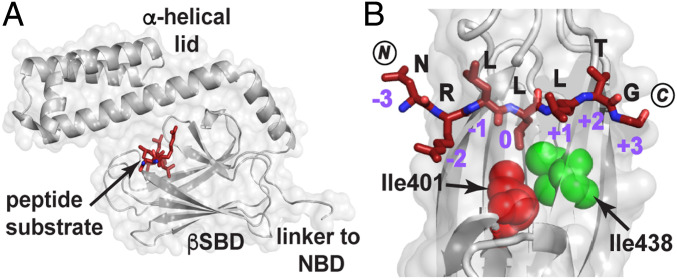
Fig. 1.
How the DnaK SBD binds a model peptide. (A) The crystal structure of the SBD of DnaK (gray) bound to the model peptide NR (NRLLLTG; maroon; PDB ID code 1DKZ) showing the peptide bound to a cleft on the β-subdomain covered by the α-helical lid (11). (B) Top view of the SBD substrate binding cleft showing the mode of binding of NR to the five pockets created by the topography of this domain. Note in particular the deep 0th pocket here occupied by L4. The SBD Ile401 (red) and Ile438 (green) are shown as spheres. Residues 507 to 603 and residues 404 to 429 are not shown to better visualize the bound peptide. (Structures here and elsewhere are depicted using PyMol [Schrodinger LCC].) NBD, nucleotide binding domain.