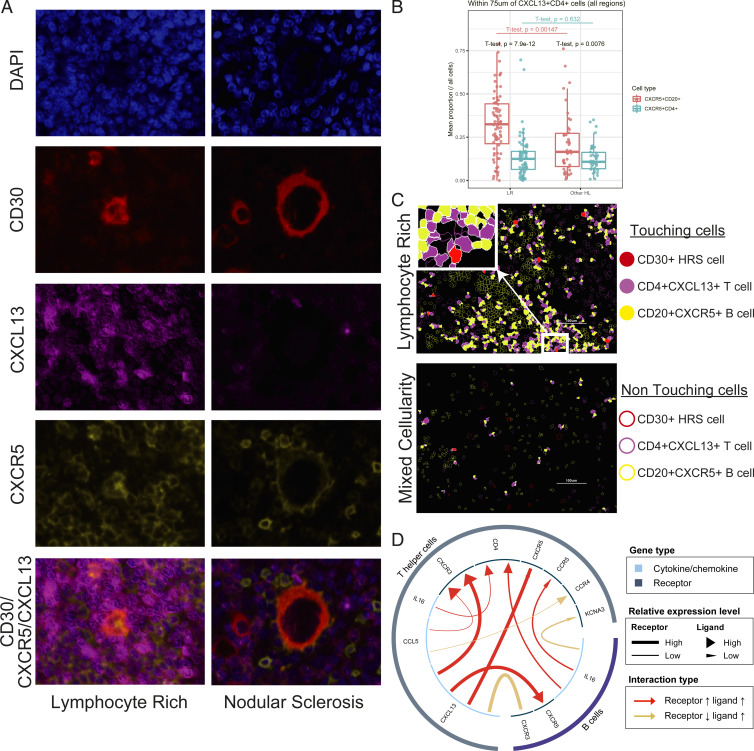
Fig. 4.
CXCL13/CXCR5 interaction in LR-CHL. (A) Multicolor IF staining (CHL05 and LRCHL16) for CD30 (red), CXCL13 (magenta), and CXCR5 (yellow), shows localization of CXCR5+ cells near CXCL13+ cells in the region surrounding HRS cells in cases with LR-CHL. CXCL13+ cells (magenta) are rarely coexpressed with CXCR5 (yellow). (B) Boxplot showing the proportion of CD20+CXCR5+ B cells and CD4+CXCR5+ T cells in the region surrounding CD4+CXCL13+ T cells (within 75 μm) for each sample, separated by pathological subtype. t tests show comparisons both within the subtypes (LR or other HL) and across subtypes (LR vs. other HL). (C) Membrane map depicting CD4+CXCL13+ T cells (magenta), CD20+CXCR5+ B cells (yellow), and CD30+ HRS cells (red). Touching cells (CD30+ HRS cells/CD4+CXCL13+ T cells and CD4+CXCL13+ T cells/CD20+CXCR5+ B cells) are represented by filled shapes. (D) An enriched positive interaction between CXCL13 on T helper cells and CXCR5 on B cells in LR-CHL was predicted using the iTALK tool.