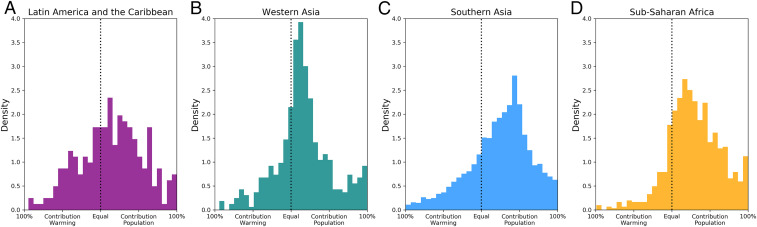
Fig. 3.
Aggregated by region, the comparative contribution to the increase in the rate of urban exposure to extreme heat due to population growth versus total urban warming largely follows regional-level urban population growth rates as shown by the examples of (A) Latin America and the Caribbean, (B) Western Asia, (C) Southern Asia, and (D) Sub-Saharan Africa.