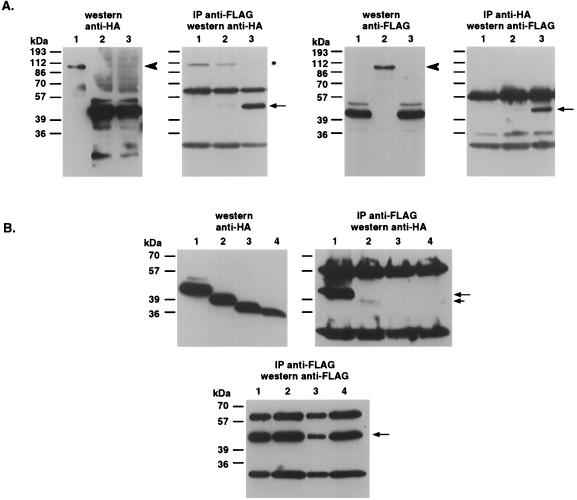
FIG. 7.
DRP-1 undergoes homodimerization via its C-terminal tail. (A) Wild-type DRP-1 undergoes specific homodimerization. 293 cells growing in 90-mm-diameter plates were cotransfected with the following constructs: lane 1, DRP-1-FLAG (5 μg) plus RFX1-ΔSmaI-HA (20 μg; used as an intrinsic control to rule out nonspecific binding of DRP-1-FLAG to HA beads or to an irrelevant gene); lane 2, RFX-ΔSmaI-FLAG plus DRP-1-HA (control to rule out nonspecific attachment of DRP-1-HA to FLAG beads or to an irrelevant gene); lane 3, DRP-1-FLAG plus DRP-1-HA. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with either anti-FLAG antibodies (left) or anti-HA antibodies (right). The total levels of transfected proteins are shown on immunoblots. (B) Truncation of C-terminal 40 amino acids of DRP-1 abolishes its homodimerization. Lanes 1 to 4 correspond to cotransfections (5 μg of each construct per 90-mm-diameter plate) with DRP-1-FLAG plus DRP-1-HA, DRP-1-FLAG plus DRP-1-Δ40-HA, DRP-1-FLAG plus DRP-1-Δ73-HA, and DRP-1-FLAG plus DRP-1-Δ85-HA, respectively. The lower panel quantitates the immunoprecipitation efficiency of DRP-1-FLAG with the anti-FLAG antibodies. Solid arrows, immunoprecipitated DRP-1; short arrow, immunoprecipitated DRP-1 Δ40; arrowhead, RFX-ΔSmaI; asterisk, nonspecific band.