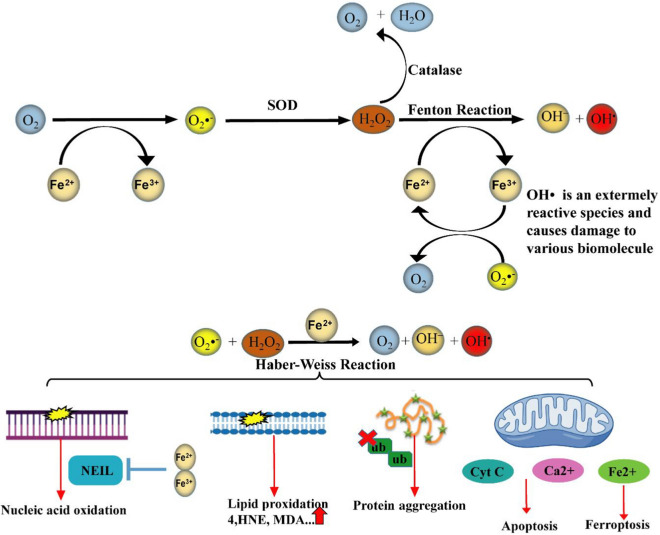
Fig. 3.
Cytotoxicity induced by iron overload: Oxygen (O2) reduction via Fe2+ produces Fe3+ and superoxide anion (O2•−). SOD enzyme converts the O2•− to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and O2. H2O2 is converted to water (H2O) via antioxidant enzymes such as catalase. In the presence of redox-active bio metals such as free iron, Fenton reaction occur by reduction of H2O2 thereby Fe3+, hydroxide (HO−), and harmful hydroxyl radical (OH•) are produced. On other hand, Fe3+ reduction via O2•− in the iron-sulfur proteins, renews Fe2+ for Fenton reaction. Accordingly, the reaction referred to the Haber–Weiss reaction which has required iron ions. Iron overload and ROS mutually reinforce each other and damage nucleic acids, lipids, proteins, and cellular compartments such as mitochondria. SOD, superoxide dismutase; HNE, hydroxynonenal; MDA, malondialdehyde; cyt C, cytochrome C; NEIL, nei like DNA glycosylase; ub, ubiquitination. This Figure was created by powerPoint and Adobe Illustrator