Table 2.
Comparison between QC and conventional iron chelators
| Iron chelating agents | Quercetin (QC) | Deferoxamine (DFO) | Deferasirox (DFX) | Deferiprone (DFP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type (source) | Natural (flavonoid) [176] | Natural (siderophore) [176] | Synthetic [176] | Synthetic [176] |
| Molecular weight | 302.236 g/mol (see Foot note link 13) | 500–900 g/mol [273] | 373 g/mol [267] | 139 g/mol [267] |
| Half-life | 11–28 h [176] | 20–30 min [270] | 8–16 h [270] | 2–3 h [270] |
| Routes of excretion | Urinary [172], fecal [171] | Urinary, fecal [270] [299] | Fecal [279] | Urinary [270] |
| Structure |
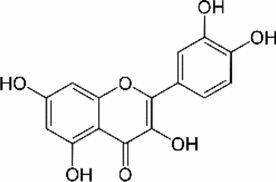
|
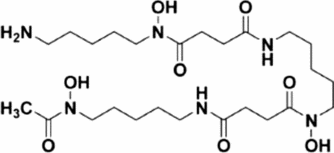
|
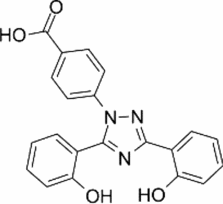
|
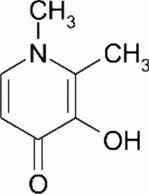
|
| Recommended dose |
500–1000 mg/day for short time (web ref, 14) 500 mg twice daily for 12 weeks (see Foot note link 15) |
20–60 mg/kg/day over 8–24 h [271] |
20–40 mg/kg/day once daily [271] |
75–100 mg/kg/day in three divided doses [271] |
| Administration | Oral and intravenously (see Foot note link 15). powder and capsule (see Foot note link 14) | Subcutaneous and intravenous [267] | Oral [279](dispersible tablet) [271] | Oral [92]tablets and solution [271] |
| Stoichiometry (chelator:iron) |
1:1 2:1 |
1:1 [292] | 2:1 [292] | 3:1 [292] |
| Adverse effects | Generally safe. at doses, more than 1000 mg/day may cause headaches, stomach aches, and tingling sensations (see Foot note link 14) | Neurological side effects at high doses [271], ocular and auditory toxicity, renal complications, growth retardation [276, 277], local allergic reactions [278] | Skin rash, gastrointestinal complications, [283], enhancing liver enzymes [271] | Gastrointestinal complications, musculoskeletal pain, neutropenia [284], and enhancing liver enzymes [271] |
| Advantages | No side effects in desirable doses and duration of medication (web ref, 14 and 15), supplied by natural sources, and longer plasma half-life than current chelators (e.g. DFO, DFX, and DFP) | Long-term experience and data available [299] | Orally active, once-daily dosing [299] and long-plasma half-life [270] | Orally active [92], low molecular weight, and high ability to penetrate tissues |
| Disadvantages | Requires high dose and low BBB crossing | Not absorption from the gastrointestinal tract [270], rapidly clearance and requires to prolong infusion [300], and poor compliance [184] | Expensive [299] and requires monitoring renal and liver function [272] | Moderate-plasma half-life [270], requires three times daily dosing and probability of negative effects [271], limited experience and data (see foot not link 16), and requires assessment of complete blood counts [270] |
| FDA approval | No | Yes [278] | Yes [278] | Yes, except the United States and Canada [270] |
