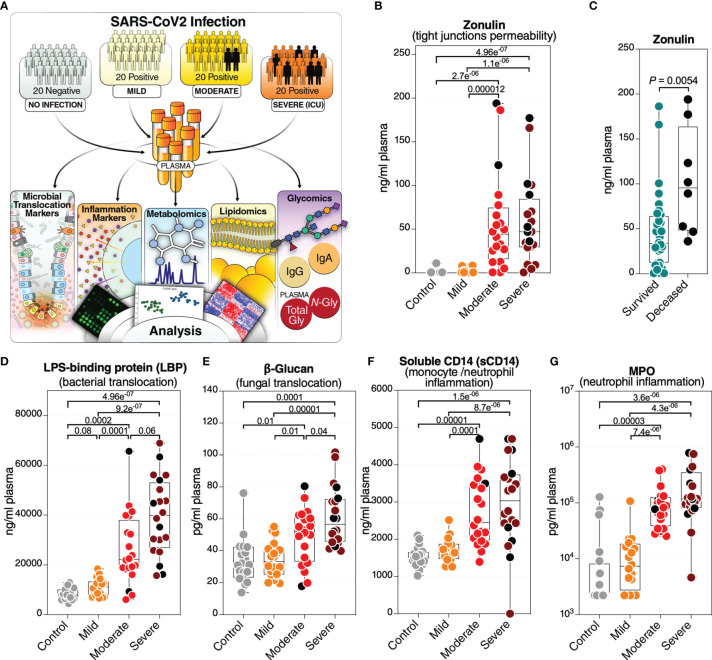
Figure 1.
Severe COVID-19 is associated with an increase in markers of tight junction permeability and microbial translocation. (A) An overview of the main cohort study design; moderate and severe patients were hospitalized; severe indicates patients in the intensive care unit. (B) Levels of plasma zonulin, are higher during moderate and severe COVID-19 compared to mild COVID-19 or controls. Kruskal–Wallis test was used for statistical analysis. False discovery rate (FDR) was calculated using the Benjamini-Hochberg method. Symbols in black indicate deceased. (C) Zonulin levels are higher in hospitalized COVID patients (n=40) who eventually died from COVID-19 (n=8) compared to survivors (n=32). Nominal P-value was calculated using the Mann–Whitney U test. (D–G) Levels of LBP (D), β-Glucan (E), sCD14 (F), and MPO (G), are higher during severe COVID-19 compared to mild COVID-19 or controls. Kruskal–Wallis test was used for statistical analysis. FDR was calculated using Benjamini-Hochberg method. Black dots indicate deceased.