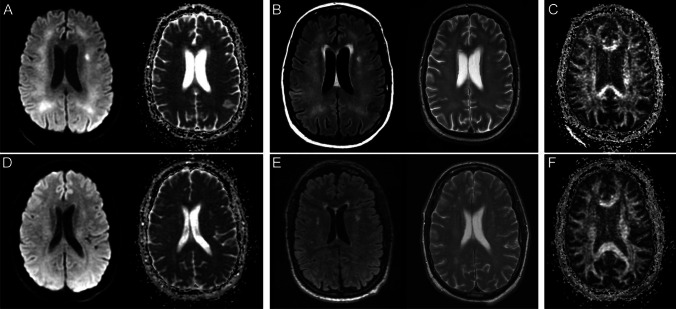
Fig. 2.
Brain MR images of a critically ill patient (case 2) with acute COVID-19 infection (A–C) and follow-up brain MRI 11-month post-discharge (D–F). A Paired axial diffusion-weighted image (DWI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map show confluent restricted diffusion in the bilateral supratentorial white matter. B Paired axial FLAIR and T2 images through the same level show confluent symmetric T2/FLAIR hyperintensity in the supratentorial white matter with relative sparing of the subcortical U-fibers, corresponding to the areas of restricted diffusion. C Axial fractional anisotropy map shows no associated disruption of white matter tracts. D Paired axial diffusion-weighted image (DWI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map on follow-up brain MRI show resolution of restricted diffusion in the supratentorial white matter. E Paired axial FLAIR and T2 images on follow-up MRI show resolution of confluent T2/FLAIR hyperintensity in the supratentorial white matter with scattered multifocal T2/FLAIR hyperintense foci in the periventricular and subcortical white matter, which may reflect sequelae of leukoencephalopathy. There was no evidence of leukoencephalomalacia. F Axial fractional anisotropy map shows no associated disruption of white matter tracts