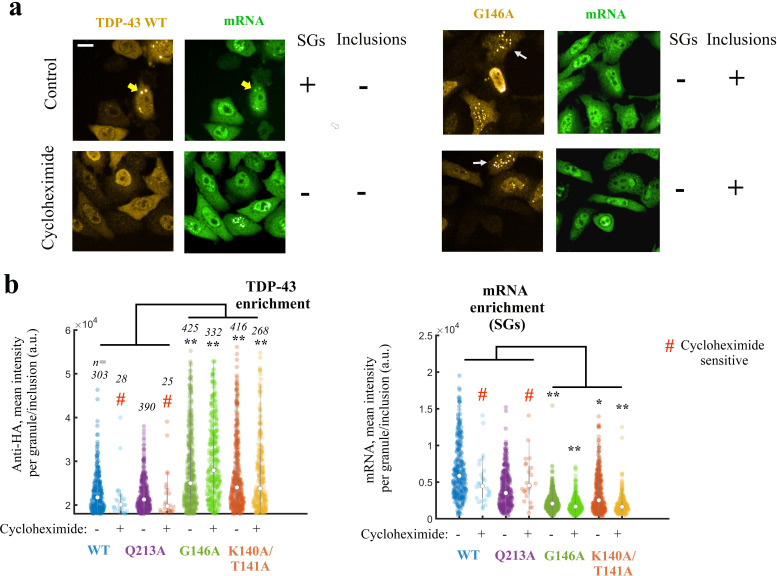
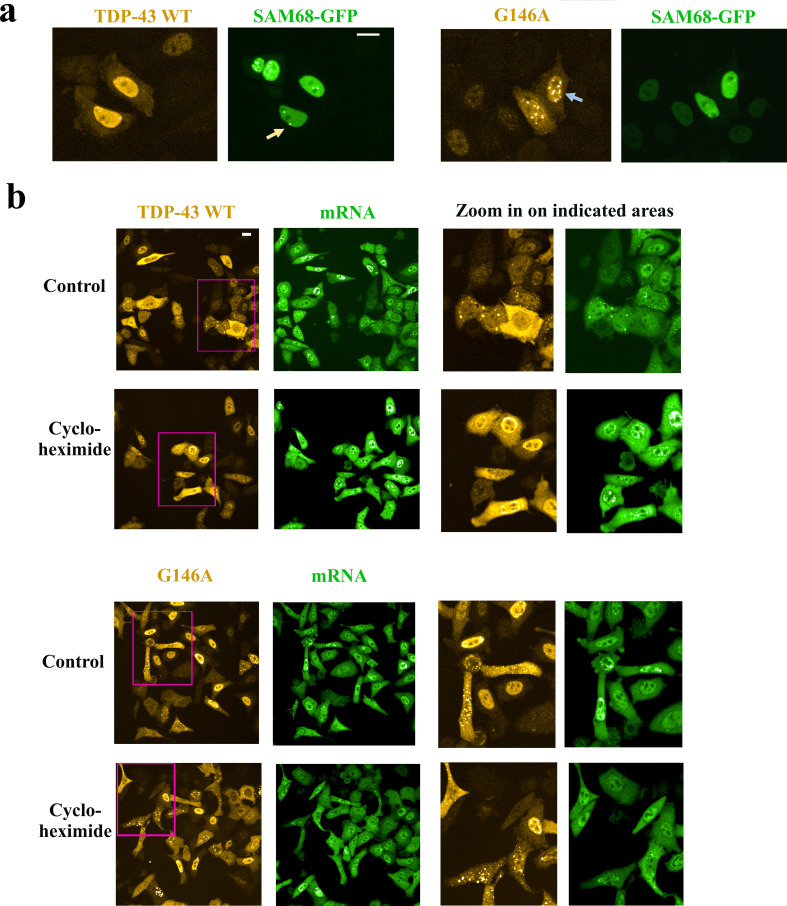
Figure 7. Expressing TDP-43 mutants with an altered cooperative binding mRNA in HeLa cells leads to the formation of mRNA-poor TDP-43 condensates in small fraction of cells.
(a) Subcellular distribution of wild-type TDP-43 or G146A mutant. Cycloheximide treatment was used to dissociate stress granules in the cell cytoplasm, when indicated in the figure. Wild-type TDP-43 is generally homogenously distributed in the cytoplasm but can be also found in cytoplasmic mRNA-rich stress granules (yellow head-arrows). G146A mutant is also generally homogenously distributed in the cytoplasm but can be found in brilliant condensates in the cytoplasm and G146A condensates do not colocalize with mRNAs (white head-arrows). Scale bar: 40 µm. Representative images of larger areas are shown in Figure 7—figure supplement 1b. (b) Violinplots representing TDP-43 (anti-HA) and mRNA (in situ hybridization with poly(dT) probes) fluorescence intensity in the cytoplasmic granules/aggregates detected under indicated conditions. Wild-type TDP-43 or Q213A mutant, a negative control, can be recruited in mRNA-rich stress granules that disappeared after cycloheximide treatment. On the other hand, K140A/T141A and G146A mutants are located in dense cytoplasmic condensates poorly enriched in mRNAs. Interestingly, K140A/T141A and G146A are not sensitive to cycloheximide. Cytoplasmic granules/aggregates were detected automatically by using Cell Profiler. n: number of granules/aggregates detected. p<0.05*; p<0.01** (paired two-sample t-test).