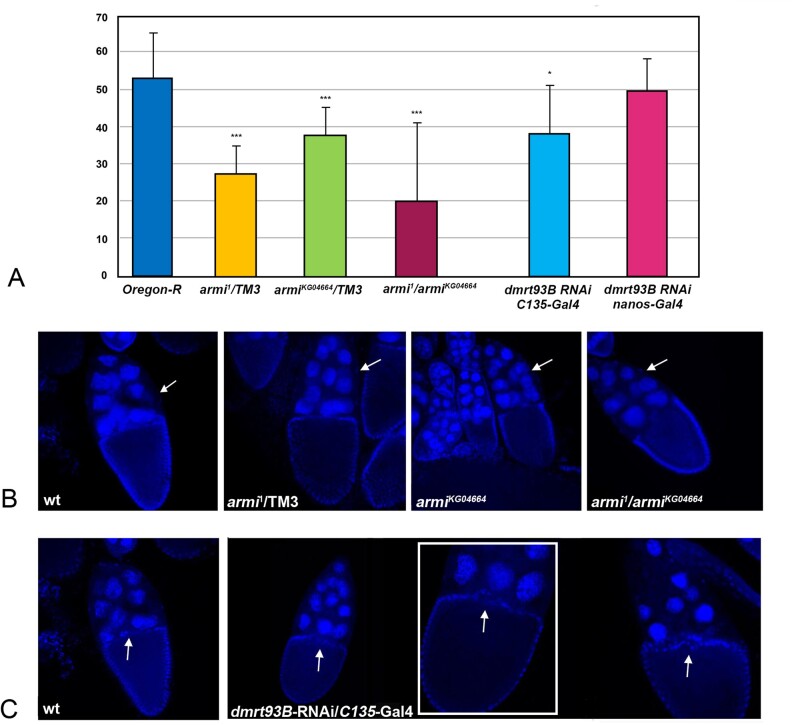
Figure 4.
Fertility tests and analysis of the egg chambers of armitage mutants and dmrt93B-RNAi. (A) Female fertility in Oregon-R control females, and in armi1/TM3, armiKG04664/TM3, armi1/armiKG04664 trans-heterozygotes, dmrt93B-RNAi/C135-Gal4 and dmrt93B-RNAi/nanos-Gal4 females (data are represented as a mean ± standard deviation, n = 20 females; ***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05: armi1/TM3 P = 0.000013; armiKG04664/TM3 P = 0.0022; armi1/armiKG04664P = 0.00038; dmrt93B-RNAi/C135-Gal4 P = 0.012; dmrt93B-RNAi/nanos-Gal4 P = 0.41). (B) wild type and armi mutants DAPI stained egg chambers, 40× magnification (images correspond to the sum of all planes that guarantees the possibility to count the nurse cells, whose position is indicated by white arrows); (C) wild type and dmrt93B-RNAi/C135-Gal4 DAPI stained egg chambers, 40× magnification (images correspond to a single plan, in order to show the border cells, whose position is indicated by white arrows, at stage 10). The zoom of the egg chamber is showed in the white panel.