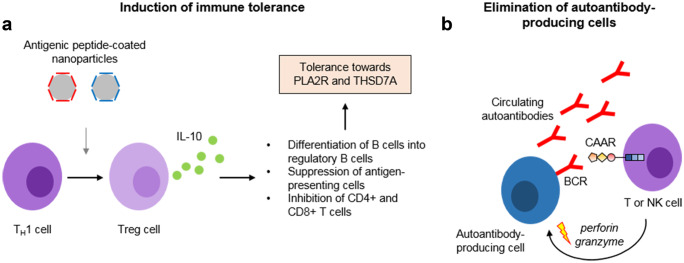
Fig. 4.
Innovative strategies to treat MN. (a) Antigen-specific tolerance can be induced using nanoparticles coated with antigen peptides corresponding to the T cell epitopes. Such nanoparticles can induce the differentiation of proinflammatory TH1 cells to regulatory T (Treg) cells, which produce interleukin-10 (IL-10). IL-10 induces the differentiation of B cells to regulatory B cells, the suppression of antigen-presenting cells and the inhibition of different T cell populations, collectively decreasing the immune response against the respective specific antigen. (b) Autoantibody-producing cells can be eliminated based on the specificity of the B cell receptor (BCR). The BCR is a membrane-bound antibody, corresponding to the antibody that is produced by this exact cell. T and NK cells can be transduced with chimeric autoantibody receptors, consisting of antigen fragments coupled to a transmembrane and several intracellular signaling domains. Depicted is a CAAR containing the first three domains of PLA2R, the cysteine-rich domain, the fibronectin type II domain, and the first c-type lectin domain. Binding of the CAAR-transduced cell to the BCR induces signaling events leading to the release of granzyme and perforins, which can efficiently eliminate the nearby autoantibody-producing cell