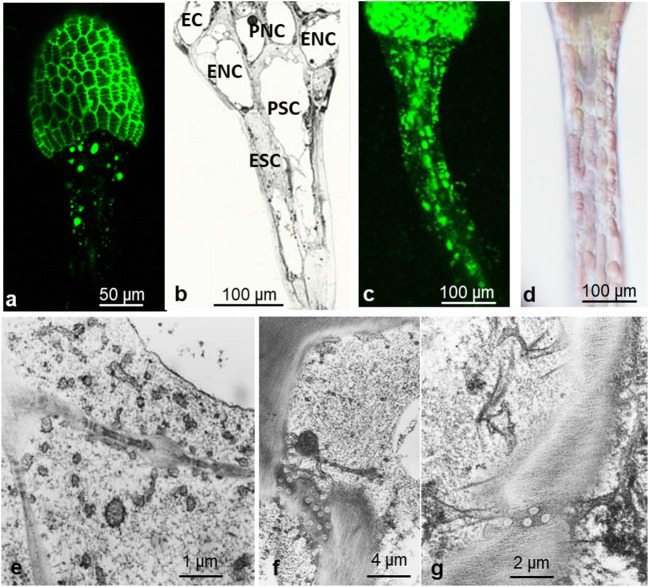
Fig. 11.
Distribution of FITC-BSA from gland head through neck cells to stalk cells. FITC-BSA occurs in endosomes of glandular cells (a) and further in epidermal and parenchymal cells of the stalk (c). In epidermal and parenchymal neck cells, it seems to accumulate within large round bodies (a). After feeding with BSA, the colorless cytoplasm of the stalk cells is swollen, whereas red vacuoles decreased in size (d; differential interference contrast). In BSA-treated stalk cells, the cytoplasm contains a large amount of small vesicles (e). A grazing section through neck and stalk in TEM shows the organization of the stalk cells (b). Plasmodesmata in transverse cell walls anchor ER (f, g). EC, endodermoid cell; ENC, epidermal neck cell; PNC, parenchymal neck cell; ESC, epidermal stalk cell; PSC, parenchymal stalk cell