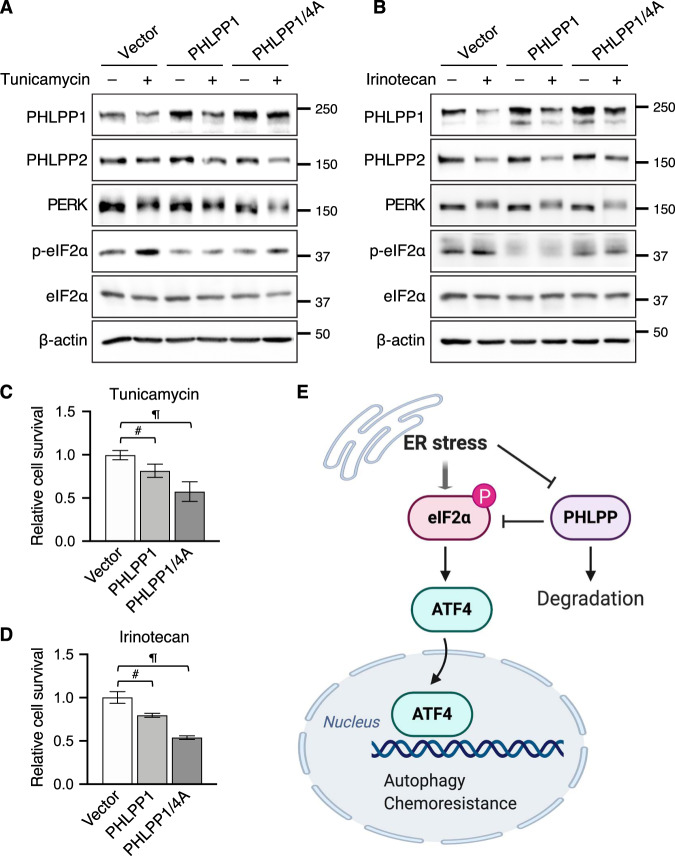
Fig. 7. Overexpression of PHLPP decreases colon cancer cell survival.
a–b HCT116 cells expressing either vector, PHLPP1 or PHLPP1/4A were treated with tunicamycin for 24 h (a) or irinotecan for 48 h (b). Cell lysates were analyzed for the expression of PHLPP1, PHLPP2, PERK, p-eIF2α, eIF2α, and β-actin using Western blot. c–d HCT116 cells expressing either vector, PHLPP1 or PHLPP1/4A were cultured 3D and treated with tunicamycin (c) or irinotecan (d) for 48 h. The relative cell survival was quantified and normalized to vector control cells. Data represent the mean ± SD (n = 3, # p < 0.01 and ¶ p < 0.0001). e A diagram shows that ER stress stimulates PHLPP degradation via a proteasome-dependent mechanism. This downregulation of PHLPP promotes the integrated stress response by enhancing eIF2α phosphorylation and ATF4-mediated activation of autophagy. Thus, PHLPP-loss represents a new mechanism underlying chemoresistance in colon cancer.