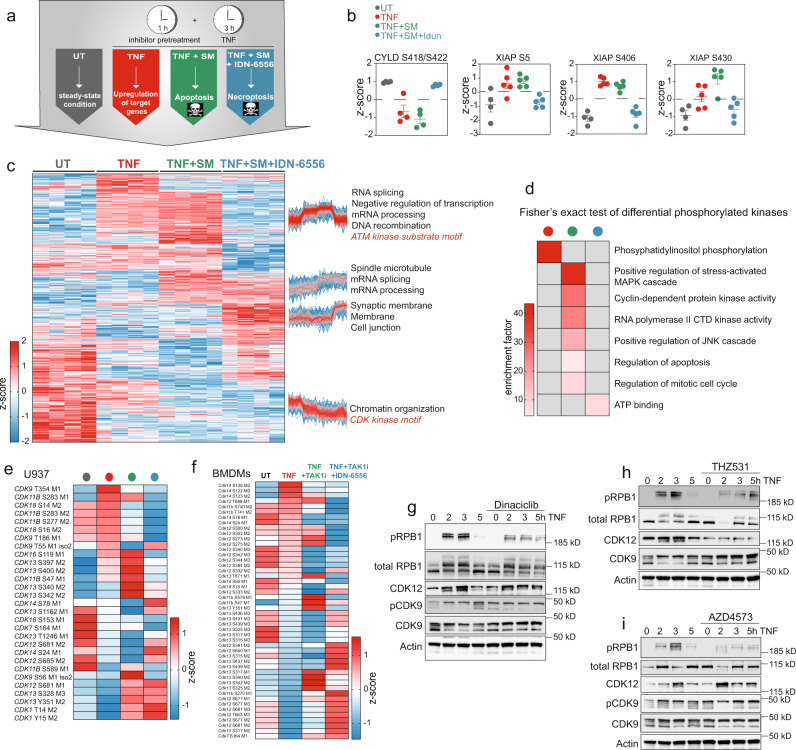
Fig. 4. TNF-induced cell death leads to a strong RNA-processing response and regulation of the phosphorylation status of CDKs.
a Experimental scheme of U937 cells that were untreated, treated with TNF (100 ng/ml, red) alone, treated with TNF and Smac mimetic (SM/Birinapant, 1.25 μM, green) to induce apoptosis, or with TNF, SM, and IDN-6556 (Emricasan, 10 μM, blue) to induce necroptosis. b Z-scored phosphosite intensities of CYLD and XIAP that are regulated upon TNF treatment, TNF-induced apoptosis, and TNF-induced necroptosis (±SEM, n = 4 biologically independent experiments). XIAP phosphosites were retrieved from a DDA dataset (Methods). c Heatmap of z-scored phosphosite intensities that are one-way ANOVA significantly regulated upon TNF treatment or TNF-induced cell death (FDR < 0.05). The profiles are color-coded according to their distance from the respective cluster center (red is close to the center, blue is further away from the center). d Fisher’s exact test on kinases with significantly regulated phosphosites upon different treatments (FDR < 0.02). e Heatmap of means of z-scored phosphosite intensities of CDKs that significantly changed upon treatment of U937 cells (one-way ANOVA, FDR < 0.05). f Heatmap of means of z-scored phosphosite intensities of CDKs that changed significantly (one-way ANOVA) upon treatment of BMDMs with TNF (red) alone, TNF, and TAK1 inhibitor (TAKi, 1 μM) to induce apoptosis (green) or TNF, TAK1i, and the caspase inhibitor IDN-6556 to induce necroptosis (blue). Untreated cells (UT) served as controls (FDR < 0.05). g–i Immunoblots of U937 cells stimulated with TNF as indicated or in combination with CDK inhibitors Dinaciclib (6 nM) (g), THZ531 (200 nM) (h), and AZD4573 (6 nM) (i) and probed with antibodies against phosphorylated (S2) and total (N-terminal) RPB1, phosphorylated (T186), and total CDK9, CDK12, and β-actin (n = 2 biologically independent experiments). Source data are provided as source file.